Understanding Reasoning LLMs
Subtitle: Methods and Strategies for Building and Refining Reasoning Models
Date: JUL 19, 2025
URL: https://magazine.sebastianraschka.com/p/understanding-reasoning-llms
Likes: 1,239
Image Count: 18
Images
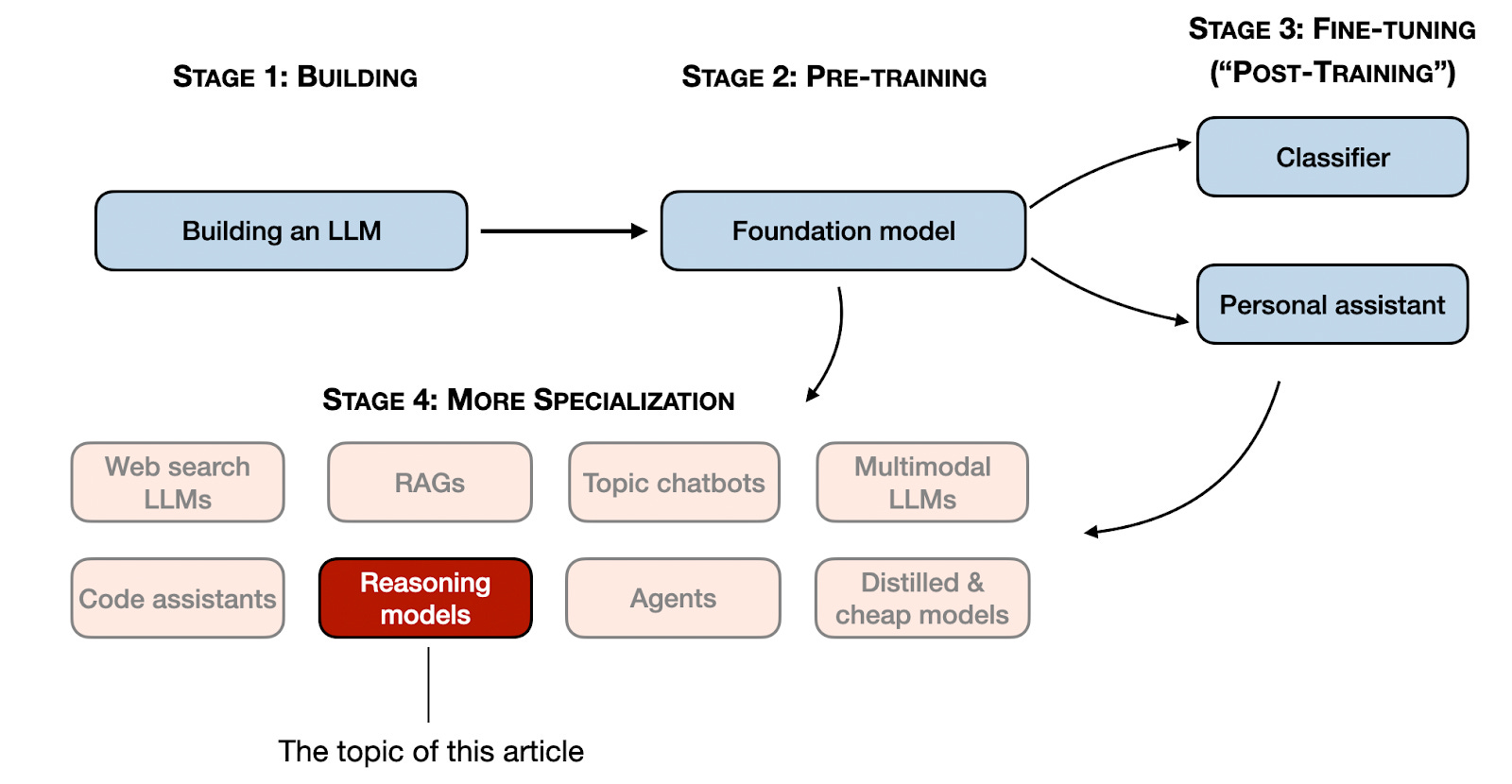
Figure - Caption: Stages 1-3 are the common steps to developing LLMs. Stage 4 specializes LLMs for specific use cases.
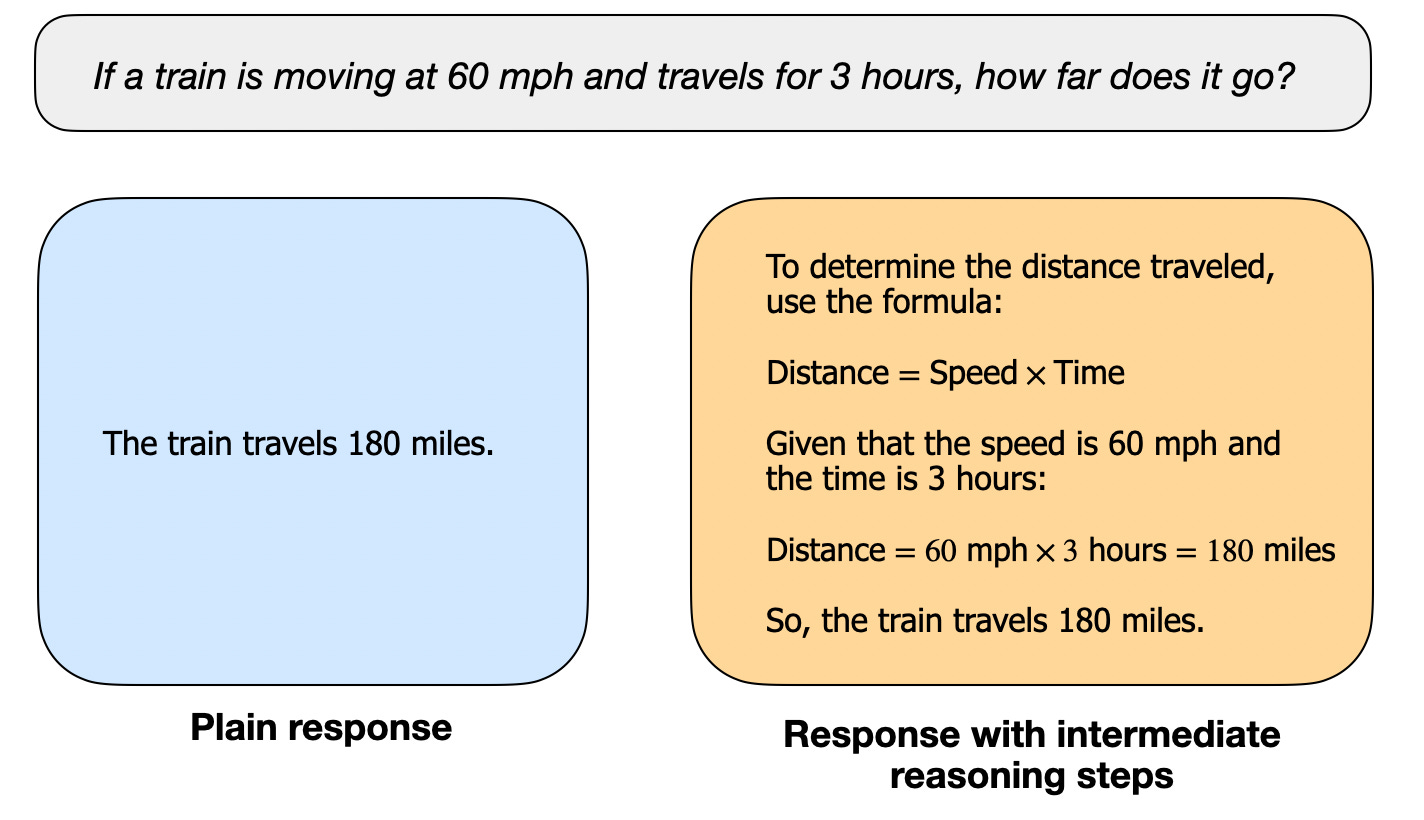
Figure - Caption: A regular LLM may only provide a short answer (as shown on the left), whereas reasoning models typically include intermediate steps.
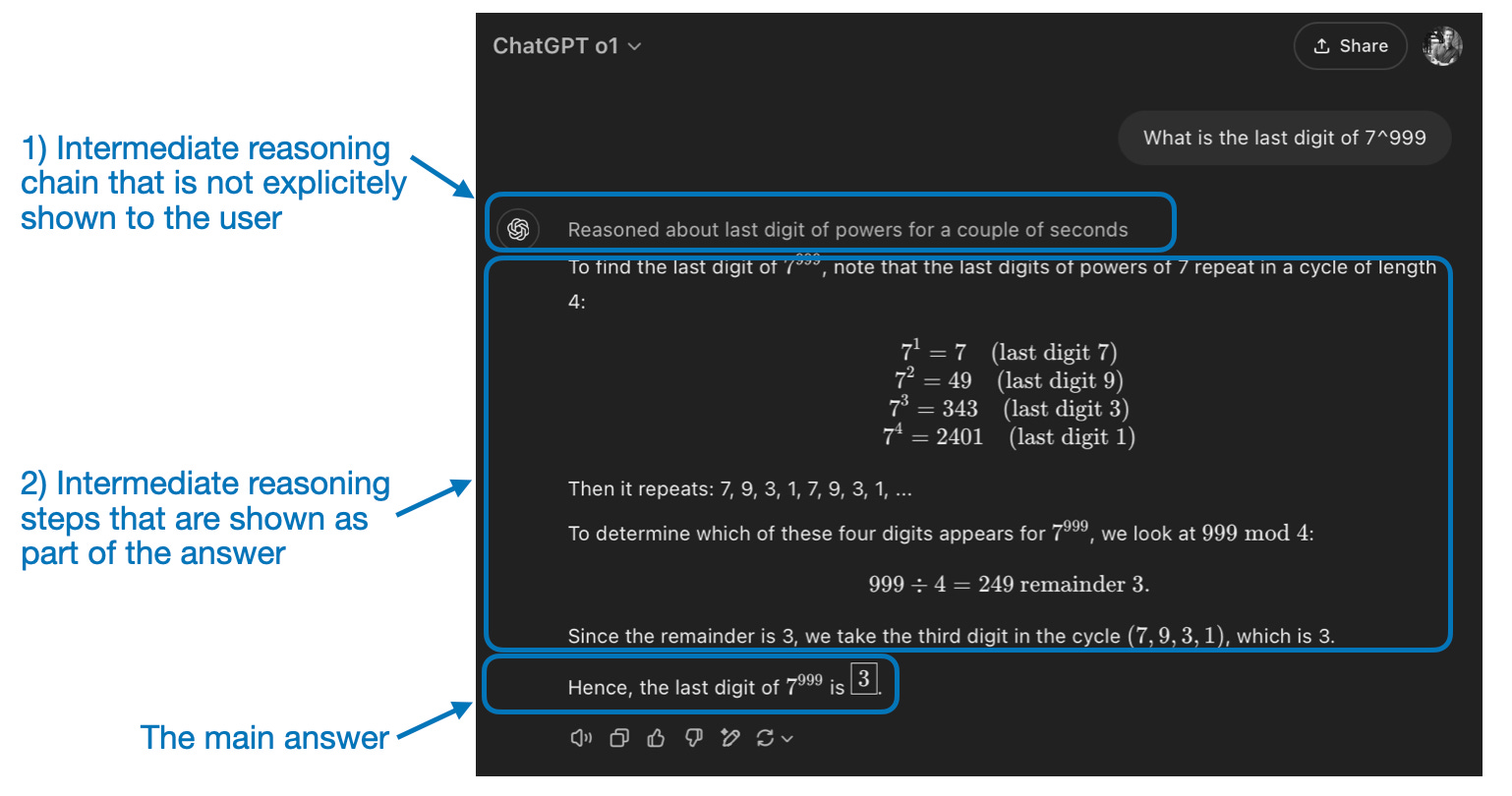
Figure - Caption: “Reasoning” is used at two different levels: 1) processing the input and generating via multiple intermediate steps and 2) providing some sort of reasoning as part of the response to the user.

Figure - Caption: The key strengths and weaknesses of reasoning models.
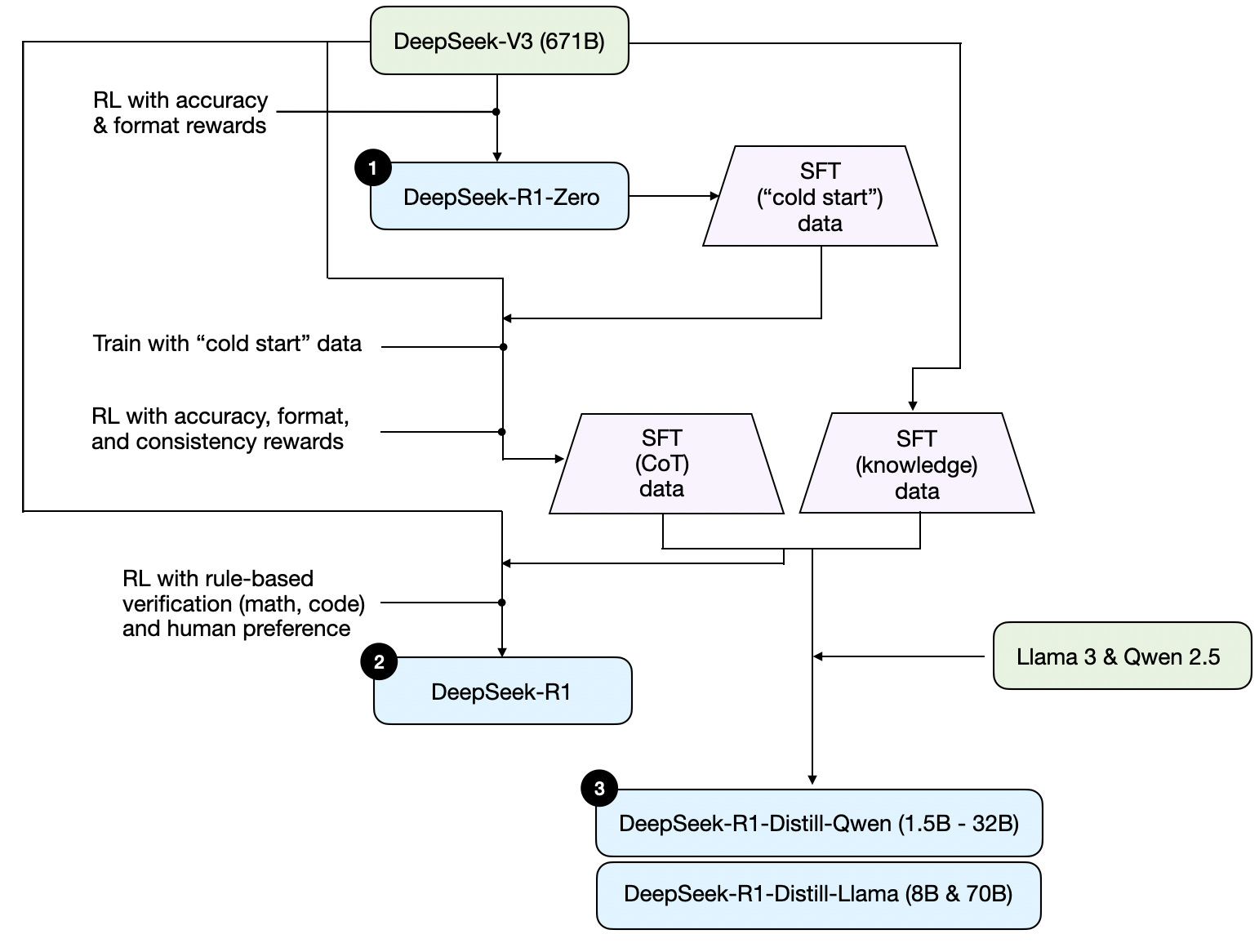
Figure - Caption: Development process of DeepSeeks three different reasoning models.

Figure - Caption: An example of classic CoT prompting from the 2022 Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Reasoners paper.
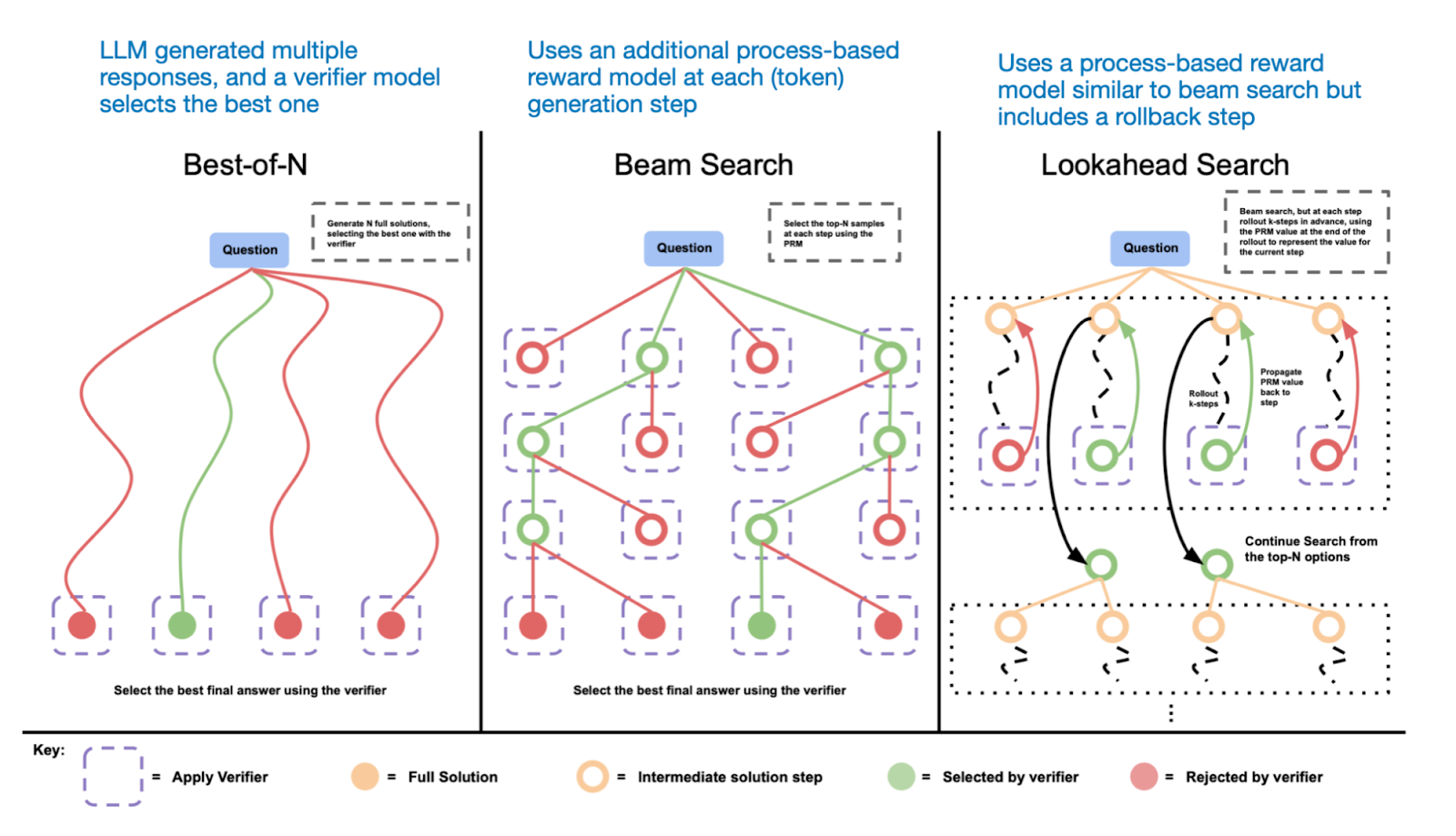
Figure - Caption: Different search-based methods rely on a process-reward-based model to select the best answer.
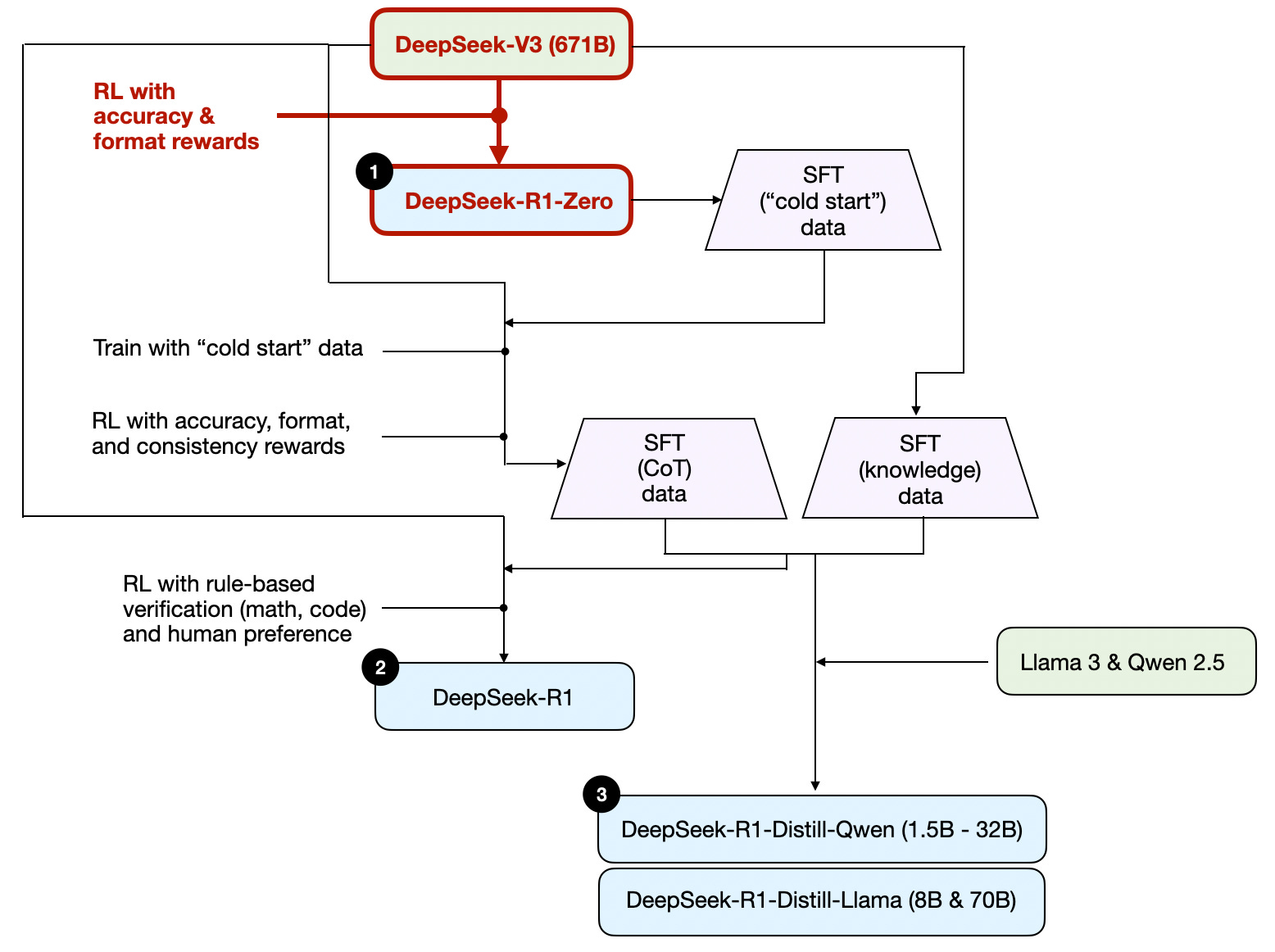
Figure - Caption: The development process of DeepSeek-R1-Zero model.
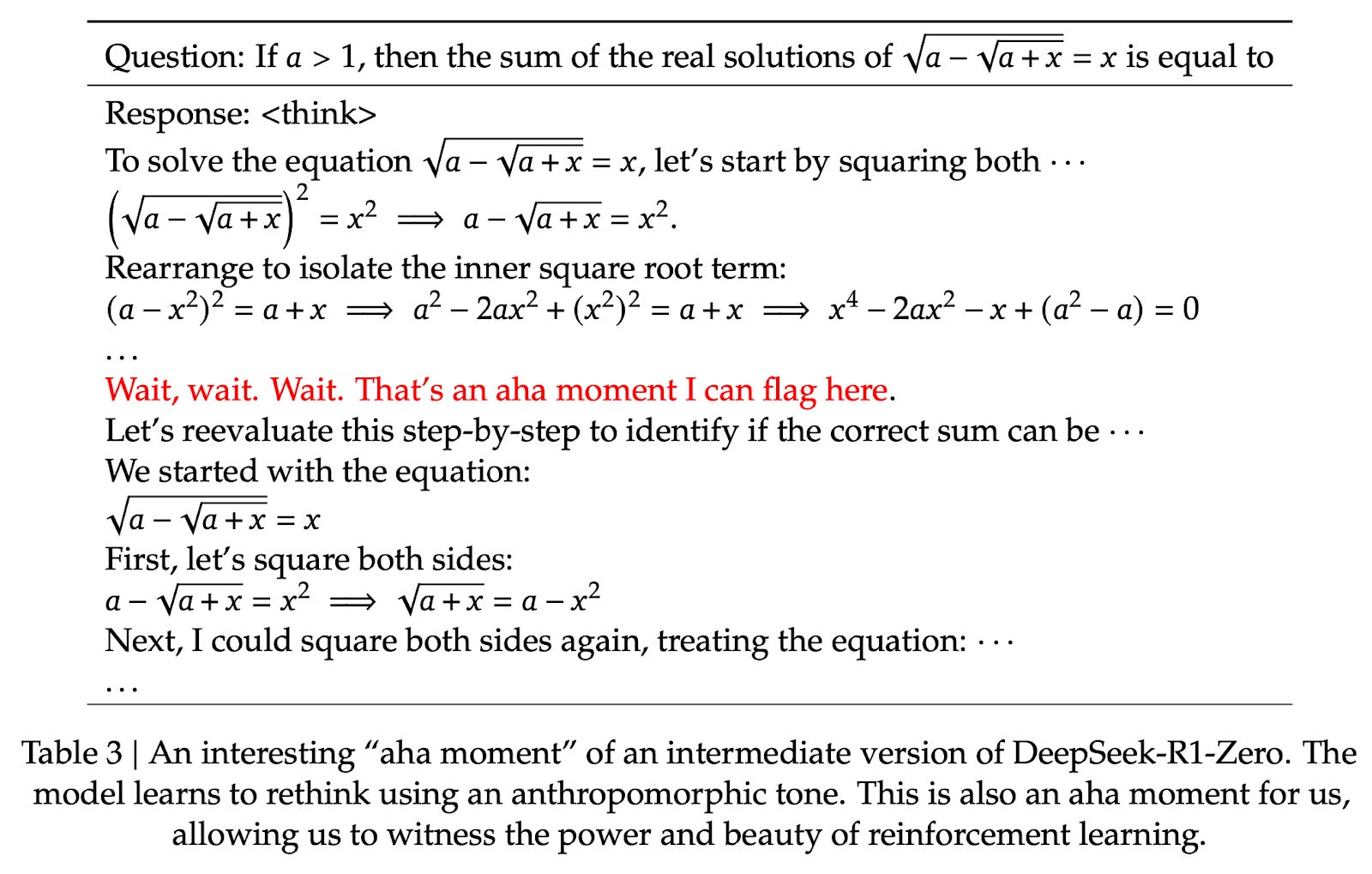
Figure - Caption: A figure from the DeepSeek R1 technical report showing the emergence of the “Aha” moment.
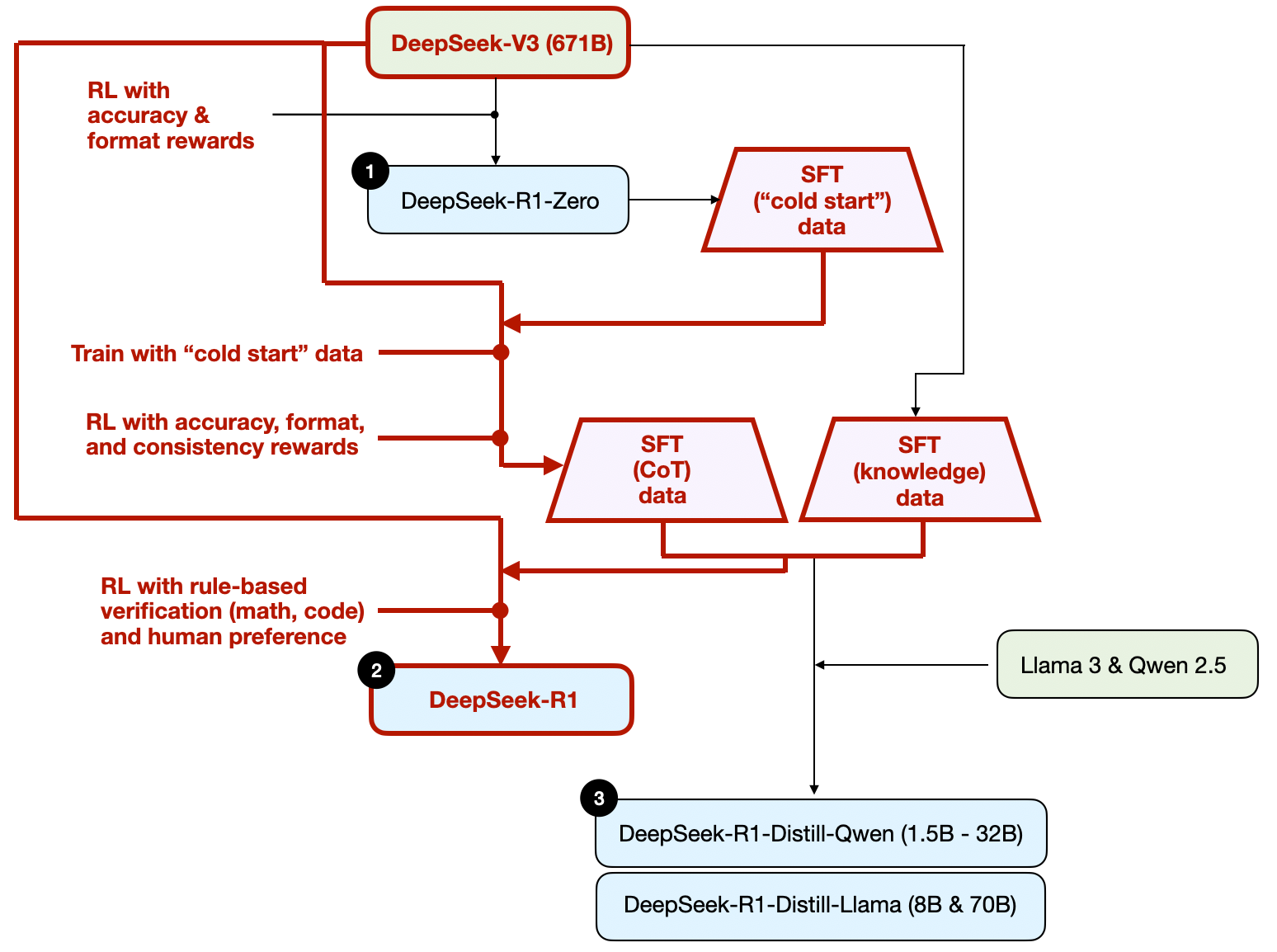
Figure - Caption: The development process of DeepSeek-R1 model.
Full Text Content
This article describes the four main approaches to building reasoning models, or how we can enhance LLMs with reasoning capabilities.
Table of Contents
- How do we define “reasoning model”?
- When should we use reasoning models?
- A brief look at the DeepSeek training pipeline
- The 4 main ways to build and improve reasoning models
- 4.1 Inference-time scaling
- 4.2 Pure reinforcement learning (RL)
- 4.3 Supervised finetuning and reinforcement learning (SFT + RL)
- 4.4 Pure supervised finetuning (SFT) and distillation
- Conclusion
- Thoughts about DeepSeek R1
- Developing reasoning models on a limited budget
- Sky-T1 ($450)
- TinyZero (<$30)
- Journey Learning
Key Concepts
Definition of Reasoning Model
- Process of answering questions that require complex, multi-step generation with intermediate steps
- Two levels of “reasoning”:
- Processing input and generating via multiple intermediate steps
- Providing reasoning as part of the response to the user
When to Use Reasoning Models
Strengths: - Complex multi-step problems - Advanced math - Challenging coding tasks - Puzzles and riddles
Weaknesses: - More expensive to run - More verbose - Prone to “overthinking” errors - Not needed for simple tasks (summarization, translation, QA)
The 4 Main Approaches
- Inference-Time Scaling
- No additional training required
- Increases inference costs
- Examples: Chain-of-thought prompting, majority voting, beam search
- OpenAI o1 likely uses this (explains higher cost)
- Pure Reinforcement Learning
- DeepSeek-R1-Zero approach
- No SFT stage (“cold start”)
- Two types of rewards:
- Accuracy reward (LeetCode compiler for code, deterministic for math)
- Format reward (LLM judge for
tags)
- Key finding: “Aha moment” - reasoning emerged without explicit training
- SFT + RL (The Blueprint)
- DeepSeek-R1 approach
- Steps:
- Start with R1-Zero → generate “cold-start” SFT data
- Instruction fine-tuning
- RL stage (accuracy + format + consistency rewards)
- Generate 600K CoT + 200K knowledge SFT examples
- Final instruction fine-tuning
- Final RL stage
- Pure SFT / Distillation
- DeepSeek-R1-Distill
- Fine-tune smaller models (Llama 8B/70B, Qwen 0.5B-32B) on SFT data from larger models
- Not traditional knowledge distillation (no logits)
- Key finding: Distillation more effective than pure RL for smaller models
Budget-Friendly Approaches
Sky-T1 ($450) - 32B model trained on only 17K SFT samples - Performs roughly on par with o1 - Pure SFT approach
TinyZero (<$30) - 3B parameter model - Replicates DeepSeek-R1-Zero approach - Shows emergent self-verification abilities
Journey Learning - Alternative to “shortcut learning” - Includes incorrect solution paths in SFT data - Model learns from mistakes - May reinforce self-correction abilities