LLM Research Papers: The 2025 List (July to December)
Date: JUL 19, 2025
URL: https://magazine.sebastianraschka.com/p/llm-research-papers-2025-part2
Image Count: 16
Images

Figure - Caption: The State Of LLMs 2025: Progress, Progress, and Predictions

Figure - Caption: The State of Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
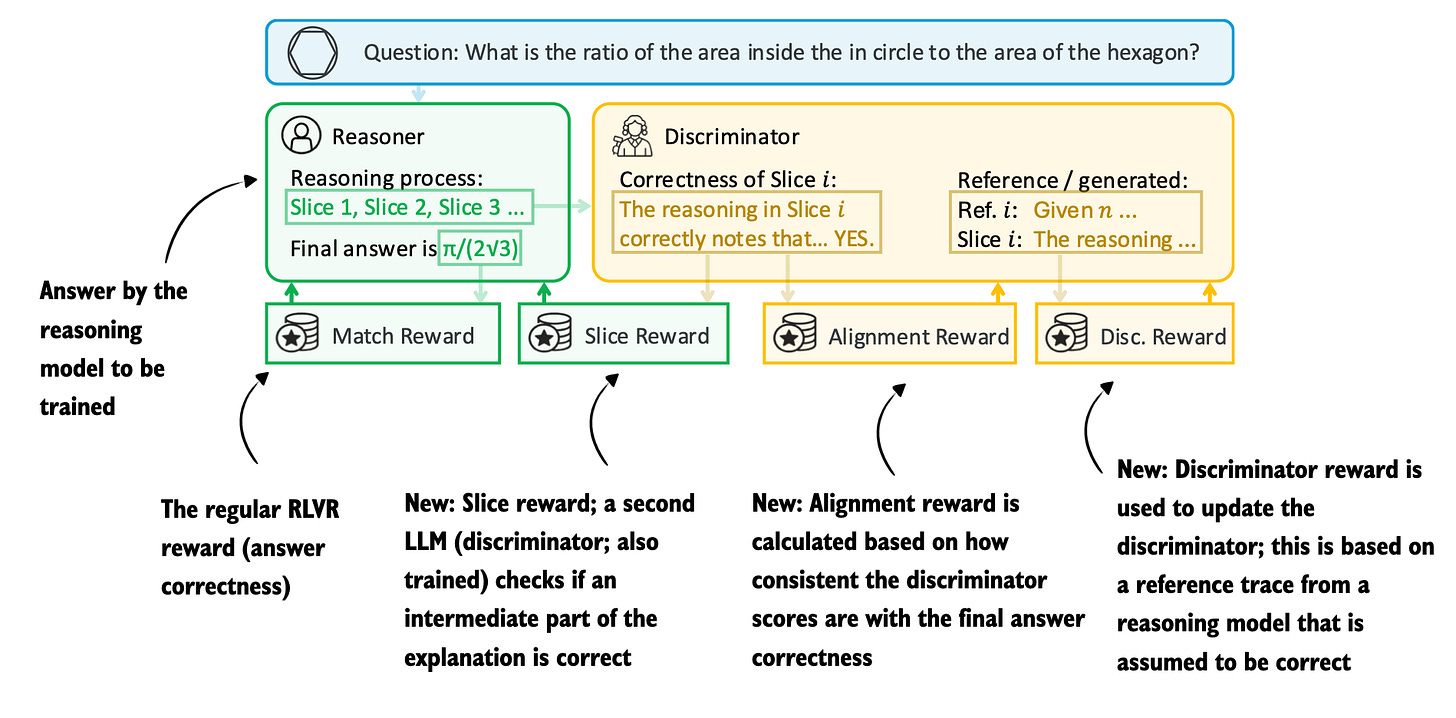
Figure - Caption: Figure 1: Annotated figure from Generative Adversarial Reasoner: Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Adversarial Reinforcement Learning
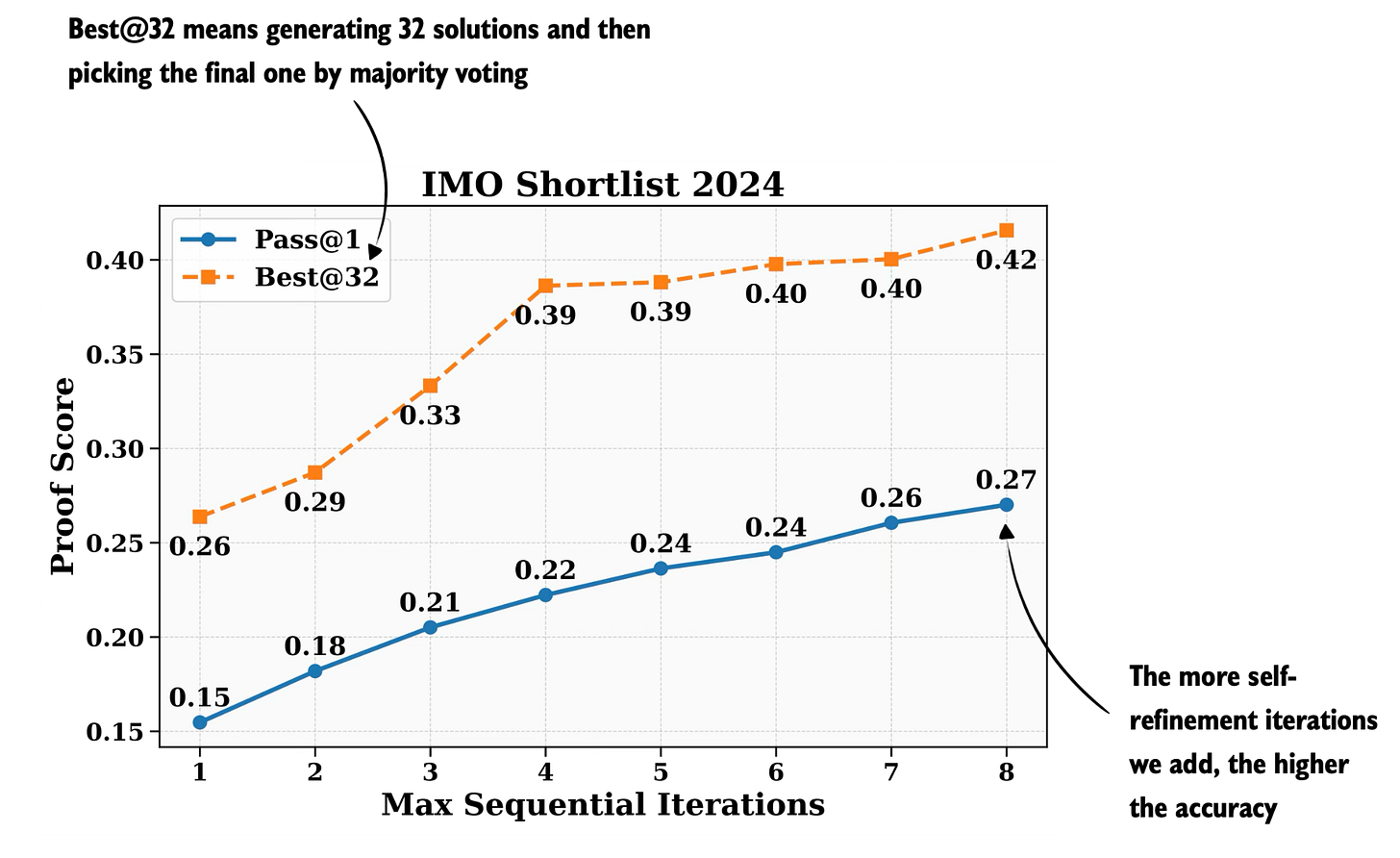
Figure - Caption: Figure 2: Improvement via two types of inference scaling, (1) self-consistency and (2) self-refinement. Annotated figure from the DeepSeekMath-V2: Towards Self-Verifiable Mathematical Reasoning paper
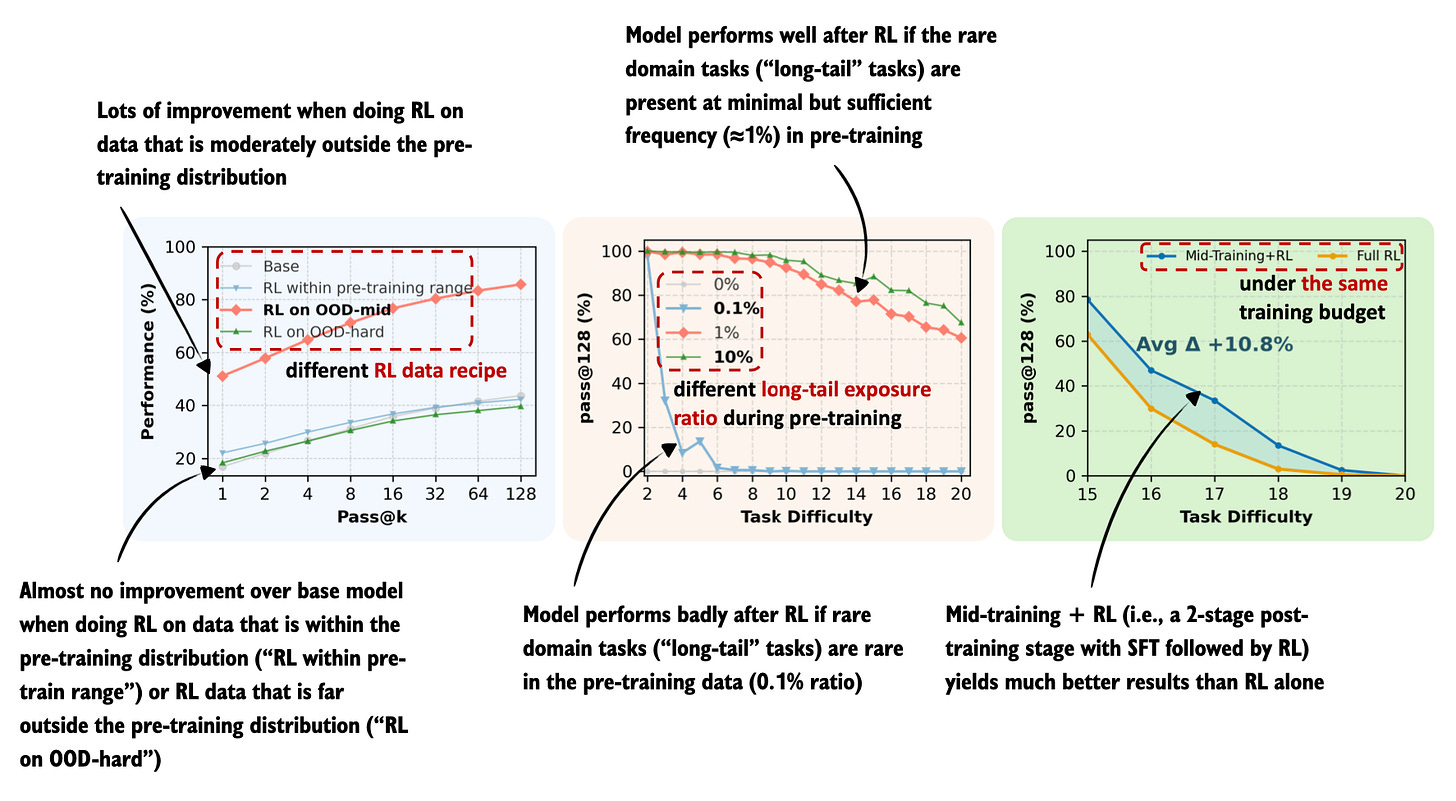
Figure - Caption: Figure 3: Annotated figure from the On the Interplay of Pre-Training, Mid-Training, and RL on Reasoning Language Models paper
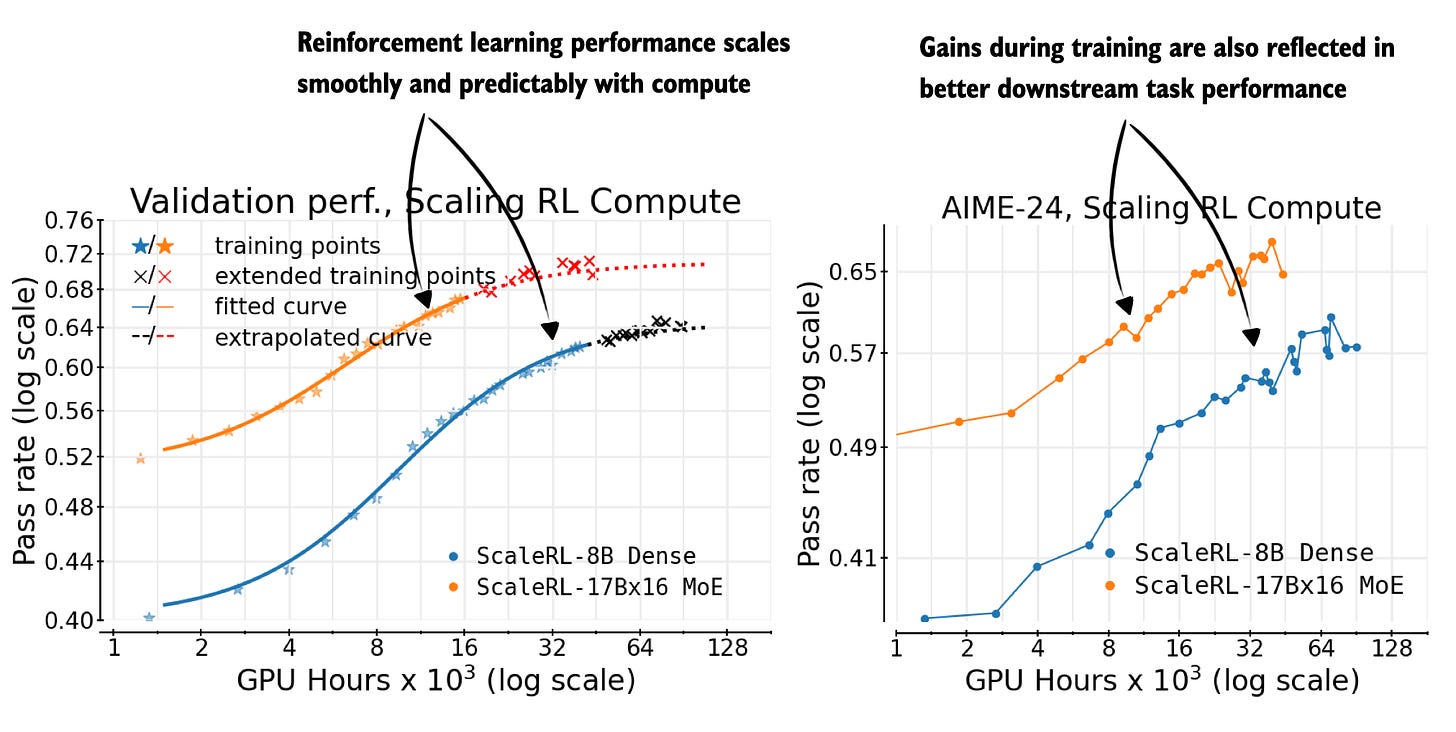
Figure - Caption: Figure 4: Annotated figure from The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs
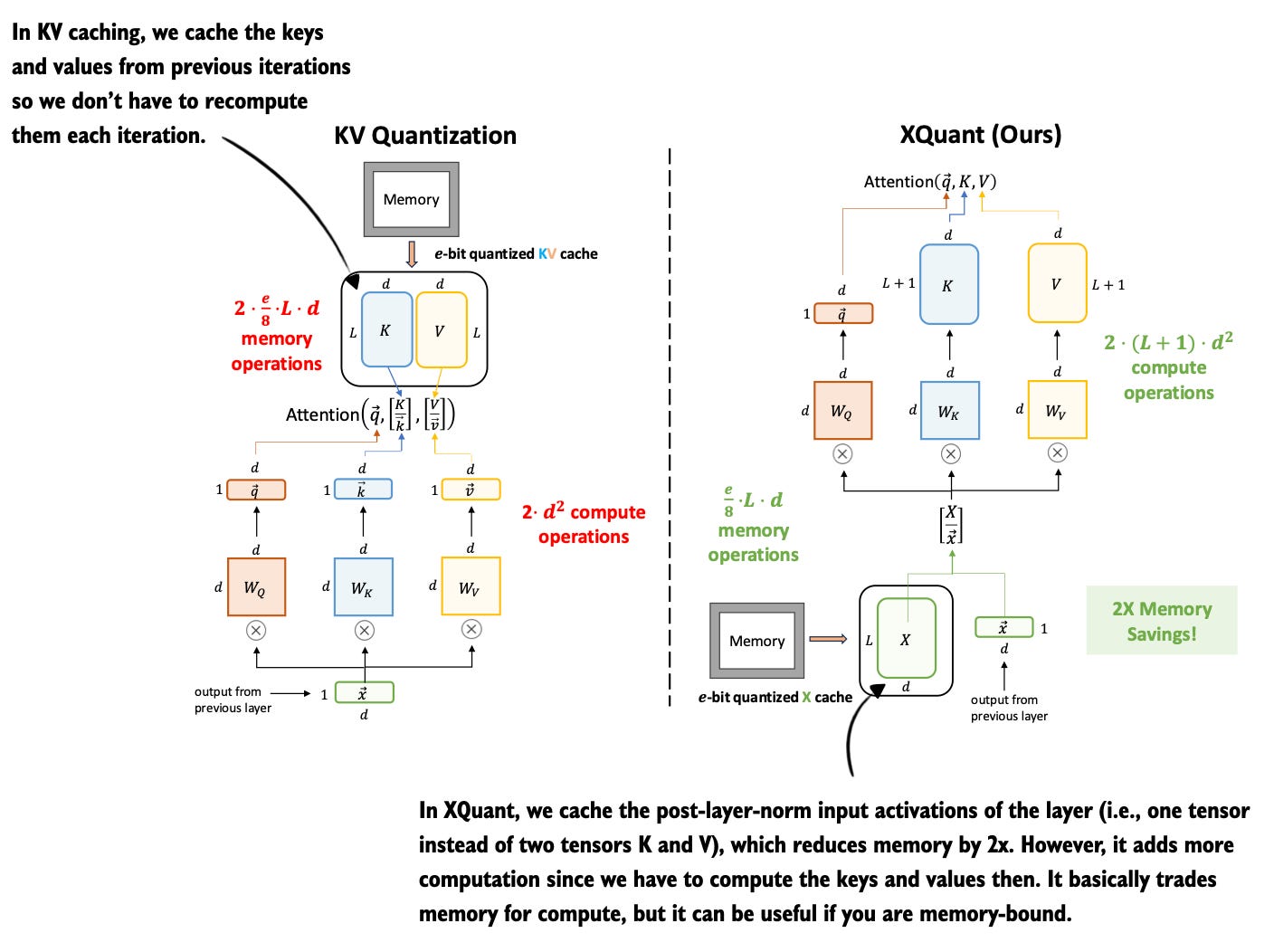
Figure - Caption: Figure 5: Annotated figure from XQuant: Breaking the Memory Wall for LLM Inference with KV Cache Rematerialization
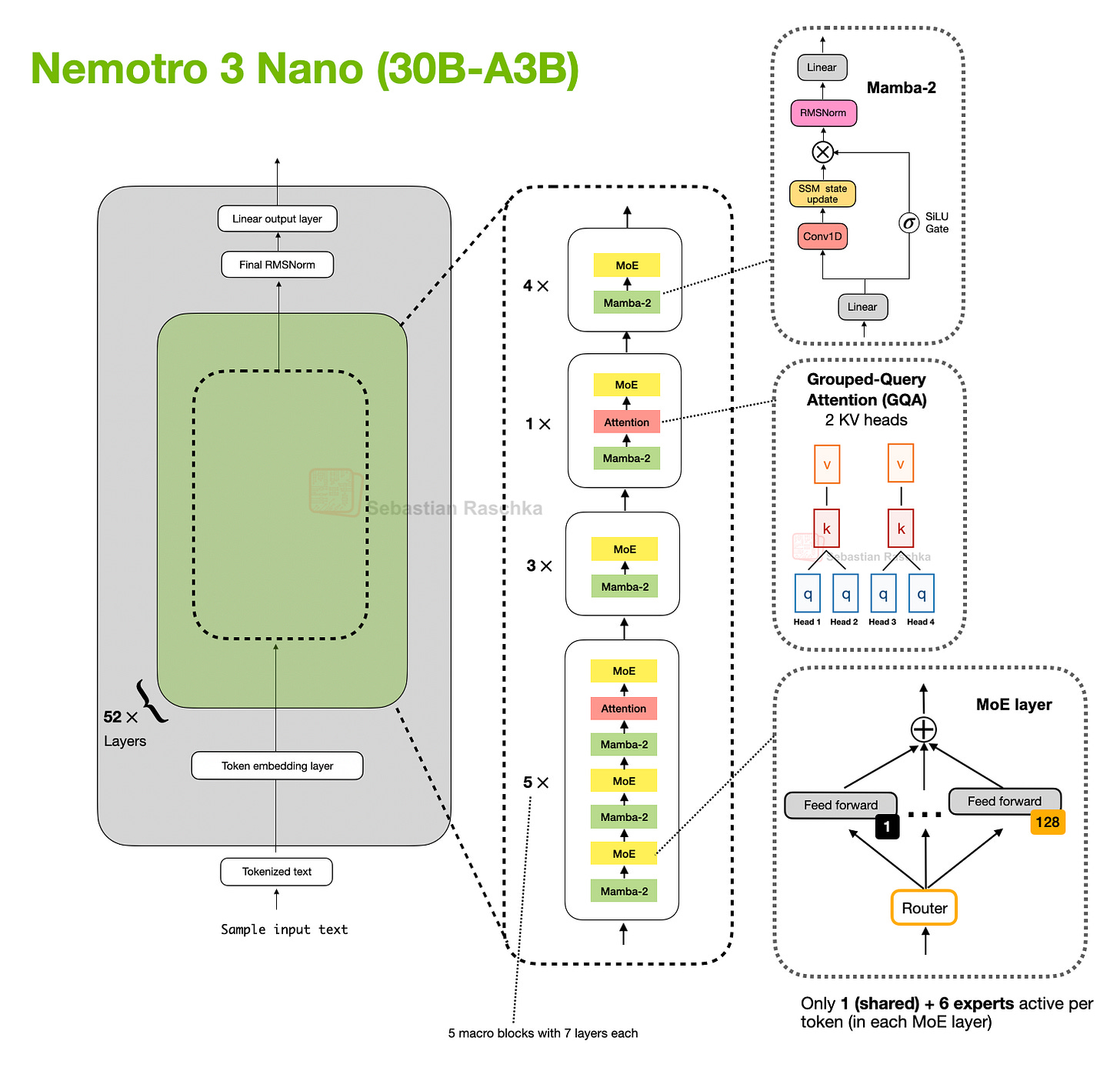
Figure - Caption: Figure 6: The NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Nano transformer-mamba hybrid architecture described in Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Model for Agentic Reasoning
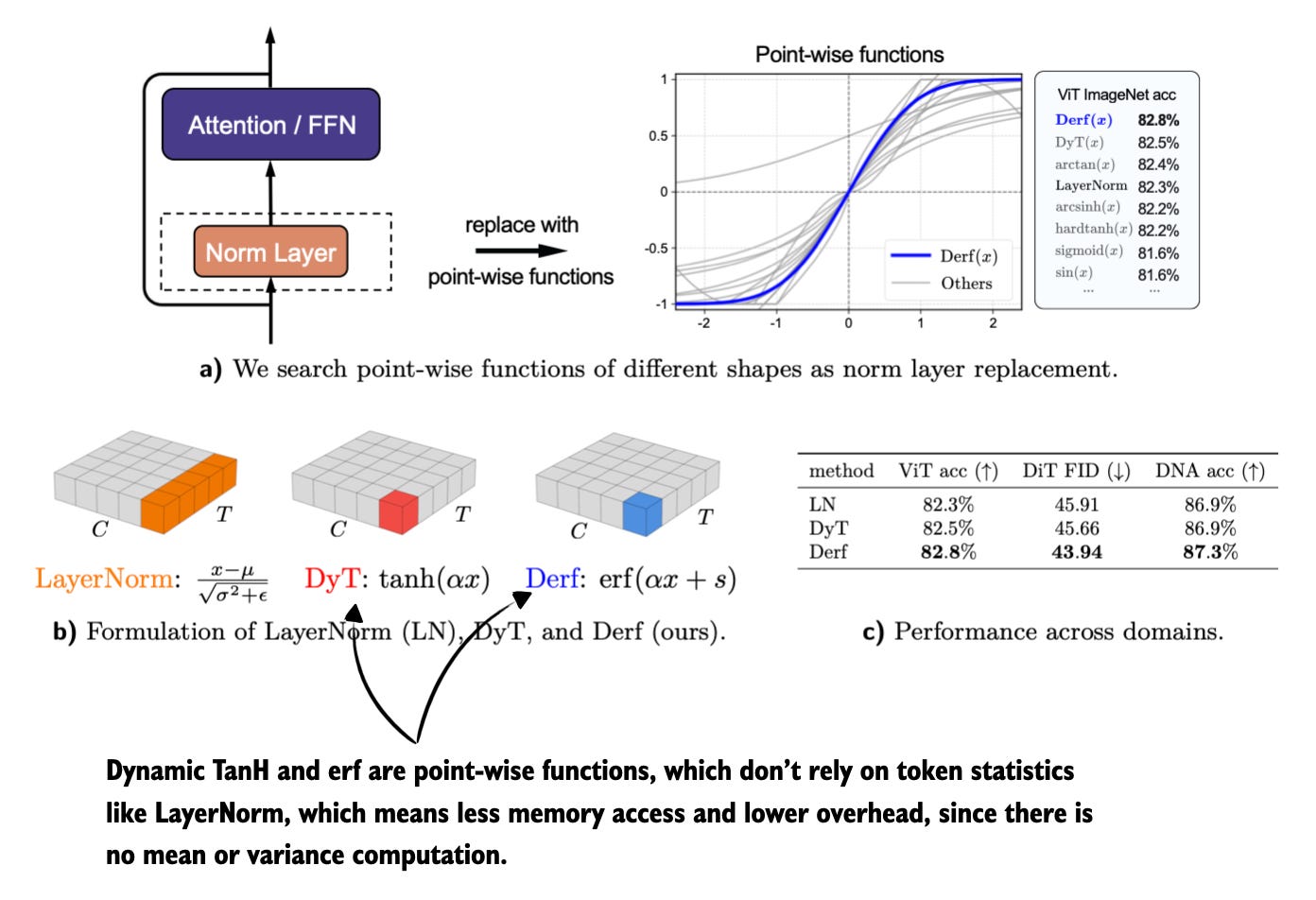
Figure - Caption: Figure 7: Annotated figure from Stronger Normalization-Free Transformers

Figure
- Caption: Figure 8: Annotated figure from Small Batch Size Training for Language Models: When Vanilla SGD Works, and Why Gradient Accumulation Is Wasteful
Figure
- Caption: Beyond Standard LLMs
Figure
- Caption: Figure 9: Annotated figure from Diffusion Language Models are Super Data Learners

Figure
- Caption: Understanding Multimodal LLMs
Figure
- Caption: Figure 10: Annotated figure from Thinking-while-Generating: Interleaving Textual Reasoning throughout Visual Generation
Figure
- Caption: Figure 11: Annotated figure from BeyondWeb: Lessons from Scaling Synthetic Data for Trillion-scale Pretraining
Figure
- Caption: The State Of LLMs 2025: Progress, Progress, and Predictions
Full Text Content
In June, I shared a bonus article with my curated and bookmarked research paper lists to the paid subscribers who make this Substack possible.
In a similar vein, as a thank-you to all the kind supporters, I have prepared a list below of the interesting research articles I bookmarked and categorized from July to December 2025.
I skimmed over the abstracts of these papers but only read a very small fraction. However, I still like to keep collecting these organized lists as I often go back to them when working on a given project.
By the way, I was also working on my annual LLM review article, State of LLMs 2025: Progress, Problems, and Predictions, which I published today as well. You can find it here:
The State Of LLMs 2025: Progress, Progress, and Predictions SEBASTIAN RASCHKA, PHD · DECEMBER 30, 2025 Read full story
Originally, I planned to include this list in the article above. However, the article was already getting quite long, so I decided to share the list here in a separate post instead. I hope you do not mind receiving two emails today. My thinking was that splitting things up would make both articles easier to read, scan, and revisit later without getting lost in an overly long page.
The categories for this research paper list are as follows (you can use the table of contents in the web view of this article to navigate to them directly):
Reasoning Models
1a. Training Reasoning Models
1b. Inference-Time Reasoning Strategies
1c. Evaluating LLMs and/or Understanding Reasoning
Other Reinforcement Learning Methods for LLMs
Other Inference-Time Scaling Methods
Model Releases / Technical Reports
Architectures
Efficient Training
Diffusion-Based Language Models
Multimodal & Vision-Language Models
Data & Pre-training Datasets
- Reasoning Models
As you may be able to tell from the three subsections in the “reasoning models” category in the table of contents, this year, my list is very heavy on reasoning models. This is because most of my work, and my recent book, are centered around reasoning models.
Also, as I mentioned in my State of LLMs 2025 report, reasoning methods have been one of the biggest themes and drivers of LLM progress this year (kickstarted by DeepSeek R1 in January 2025).
So, I decided to subdivide it into 3 categories: Training, inference-time scaling, and more general understanding/evaluation.
1a. Training Reasoning Models
This subsection focuses on training strategies designed to improve reasoning abilities in LLMs. In the first half of the year (January to June), much of the momentum centered around reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR). For more background on RLVR, you might like my The State of Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning article:
The State of Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning SEBASTIAN RASCHKA, PHD · APRIL 19, 2025 Read full story
In the second half of the year, RL is still a major theme, but the emphasis has shifted from “RLVR works” to “how do we make it scale and generalize”. This includes papers on better exploration and credit assignment, more stable and efficient optimization, extensions to long-context and agentic settings, and even RL-style training beyond strictly verifiable domains.
Figure 1: Annotated figure from Generative Adversarial Reasoner: Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Adversarial Reinforcement Learning
18 Dec, Generative Adversarial Reasoner: Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Adversarial Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.16917
18 Dec, INTELLECT-3: Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.16144
14 Dec, QwenLong-L1.5: Post-Training Recipe for Long-Context Reasoning and Memory Management, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.12967
8 Dec, Native Parallel Reasoner: Reasoning in Parallelism via Self-Distilled Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.07461
4 Dec, Efficient Reinforcement Learning with Semantic and Token Entropy for LLM Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.04359
3 Dec, PretrainZero: Reinforcement Active Pretraining, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.03442
17 Nov, P1: Mastering Physics Olympiads with Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.13612
11 Nov, SofT-GRPO: Surpassing Discrete-Token LLM Reinforcement Learning via Gumbel-Reparameterized Soft-Thinking Policy Optimization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.06411
9 Nov, Tiny Model, Big Logic: Diversity-Driven Optimization Elicits Large-Model Reasoning Ability in VibeThinker-1.5B, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.06221
28 Oct, Incentivizing Agentic Reasoning in LLM Judges via Tool-Integrated Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.23038
2 Oct, ExGRPO: Learning to Reason from Experience, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.02245
29 Sep, ReasoningBank: Scaling Agent Self-Evolving with Reasoning Memory, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.25140
29 Sep, DeepSearch: Overcome the Bottleneck of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards via Monte Carlo Tree Search, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.25454
24 Sep, Language Models that Think, Chat Better, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.20357
14 Sep, Trading-R1: Financial Trading with LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.11420
9 Sep, K2-Think: A Parameter-Efficient Reasoning System, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.07604
3 Sep, Emergent Hierarchical Reasoning in LLMs through Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.03646
28 Aug, rStar2-Agent: Agentic Reasoning Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.20722
27 Aug, Memory-R1: Enhancing Large Language Model Agents to Manage and Utilize Memories via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.19828
14 Aug, SSRL: Self-Search Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10874
7 Aug, Learning to Reason for Factuality, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.05618
1 Aug, ReaGAN: Node-as-Agent-Reasoning Graph Agentic Network, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.00429
21 Jul, LAPO: Internalizing Reasoning Efficiency via Length-Adaptive Policy Optimization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.15758
19 Jul, MiroMind-M1: An Open-Source Advancement in Mathematical Reasoning via Context-Aware Multi-Stage Policy Optimization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.14683
16 Jul, Scaling Up RL: Unlocking Diverse Reasoning in LLMs via Prolonged Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.12507
1b. Inference-Time Reasoning Strategies
This part of the list covers methods that improve reasoning dynamically at test time, without requiring retraining. Often, these papers are focused on trading computational performance for modeling performance.
Figure 2: Improvement via two types of inference scaling, (1) self-consistency and (2) self-refinement. Annotated figure from the DeepSeekMath-V2: Towards Self-Verifiable Mathematical Reasoning paper
15 Dec, Let’s (not) just put things in Context: Test-Time Training for Long-Context LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.13898
1 Dec, The Art of Scaling Test-Time Compute for Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.02008
27 Nov, DeepSeekMath-V2: Towards Self-Verifiable Mathematical Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.22570
11 Nov, Think-at-Hard: Selective Latent Iterations to Improve Reasoning Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.08577
16 Oct, Reasoning with Sampling: Your Base Model is Smarter Than You Think, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.14901
7 Oct, MixReasoning: Switching Modes to Think, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.06052
6 Oct, Less is More: Recursive Reasoning with Tiny Networks, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.04871
30 Aug, ParaThinker: Native Parallel Thinking as a New Paradigm to Scale LLM Test-time Compute, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.04475
25 Aug, MIRAGE: Scaling Test-Time Inference with Parallel Graph-Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning Chains, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.18260
22 Aug, Beyond Memorization: Extending Reasoning Depth with Recurrence, Memory and Test-Time Compute Scaling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.16745
21 Aug, Deep Think with Confidence, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.15260
22 Jul, Beyond Context Limits: Subconscious Threads for Long-Horizon Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.16784
11 Jul, KV Cache Steering for Inducing Reasoning in Small Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.08799
2 Jul, Test-Time Scaling with Reflective Generative Model, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.01951
1c. Evaluating LLMs and/or Understanding Reasoning
In this section, I collected papers that try to analyze (or evaluate) reasoning models in various ways, which is useful to refine and improve the current generation of LLM-based reasoning models.
Figure 3: Annotated figure from the On the Interplay of Pre-Training, Mid-Training, and RL on Reasoning Language Models paper
19 Dec, When Reasoning Meets Its Laws, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.17901
16 Dec, Universal Reasoning Model, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.14693
11 Dec, The FACTS Leaderboard: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Large Language Model Factuality, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10791
8 Dec, On the Interplay of Pre-Training, Mid-Training, and RL on Reasoning Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.07783
26 Nov, How to Correctly Report LLM-as-a-Judge Evaluations, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.21140
24 Nov, Does Reinforcement Learning Really Incentivize Reasoning Capacity in LLMs Beyond the Base Model?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.13837
24 Nov, What does it mean to understand language?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.19757
17 Nov, On the Fundamental Limits of LLMs at Scale, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.12869
11 Nov, The Path Not Taken: RLVR Provably Learns Off the Principals, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.08567
3 Nov, Towards Robust Mathematical Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.01846
28 Oct, Beyond a Million Tokens: Benchmarking and Enhancing Long-Term Memory in LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.27246
15 Oct, LLMs Can Get “Brain Rot”!, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.13928
13 Oct, Demystifying Reinforcement Learning in Agentic Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.11701
29 Sep, Thinking Sparks!: Emergent Attention Heads in Reasoning Models During Post Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.25758
26 Sep, When Does Reasoning Matter? A Controlled Study of Reasoning’s Contribution to Model Performance, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.22193
25 Sep, TrustJudge: Inconsistencies of LLM-as-a-Judge and How to Alleviate Them, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.21117
12 Sep, Is In-Context Learning Learning?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.10414
11 Sep, The Illusion of Diminishing Returns: Measuring Long Horizon Execution in LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.09677
11 Sep, All for One: LLMs Solve Mental Math at the Last Token With Information Transferred From Other Tokens, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.09650
7 Sep, Reverse-Engineered Reasoning for Open-Ended Generation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.06160
5 Sep, Talk Isn’t Always Cheap: Understanding Failure Modes in Multi-Agent Debate, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.05396
4 Sep, Why Language Models Hallucinate, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.04664
28 Aug, On the Theoretical Limitations of Embedding-Based Retrieval, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.21038
25 Aug, UQ: Assessing Language Models on Unsolved Questions, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.17580
18 Aug, Has GPT-5 Achieved Spatial Intelligence? An Empirical Study, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.13142
15 Aug, When Punctuation Matters: A Large-Scale Comparison of Prompt Robustness Methods for LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.11383
14 Aug, Why Cannot Large Language Models Ever Make True Correct Reasoning?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10265
11 Aug, Part I: Tricks or Traps? A Deep Dive into RL for LLM Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.08221
2 Aug, Is Chain-of-Thought Reasoning of LLMs a Mirage? A Data Distribution Lens, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.01191
21 Jul, Learning without training: The implicit dynamics of in-context learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.16003
19 Jul, Inverse Scaling in Test-Time Compute, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.14417
15 Jul, Chain of Thought Monitorability: A New and Fragile Opportunity for AI Safety, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.11473
14 Jul, Reasoning or Memorization? Unreliable Results of Reinforcement Learning Due to Data Contamination, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.10532
11 Jul, One Token to Fool LLM-as-a-Judge, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.08794
9 Jul, Rethinking Verification for LLM Code Generation: From Generation to Testing, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.00885
8 Jul, A Survey on Latent Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.06203
1 Jul, Does Math Reasoning Improve General LLM Capabilities? Understanding Transferability of LLM Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.00432
1 Jul, Scaling Laws Are Unreliable for Downstream Tasks: A Reality Check, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.00885
- Other Reinforcement Learning Methods for LLMs
Beyond reasoning-focused reinforcement learning (RL), there is a broader collection of work on reinforcement learning. This includes RL for LLM alignment, optimization, and deployment at scale.
So, in this section, I list papers that explore preference modeling and reward design, and alternatives and extensions to classical RLHF, as well as large-scale infrastructure and optimization techniques for training LLMs with reinforcement learning.
All in all, these papers provide context for how reinforcement learning is evolving in the LLM landscape beyond directly improving reasoning ability.
Figure 4: Annotated figure from The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs
23 Dec, Emergent temporal abstractions in autoregressive models enable hierarchical reinforcement learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.20605
24 Nov, DR Tulu: Reinforcement Learning with Evolving Rubrics for Deep Research, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.19399
20 Nov, Evolution Strategies at the Hyperscale, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.16652
18 Nov, Seer: Online Context Learning for Fast Synchronous LLM Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.14617
10 Nov, GroupRank: A Groupwise Reranking Paradigm Driven by Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.11653
15 Oct, The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.13786
9 Oct, Don’t Waste Mistakes: Leveraging Negative RL-Groups via Confidence Reweighting, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.08696
8 Oct, Hybrid Reinforcement: When Reward Is Sparse, It’s Better to Be Dense, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.07242
7 Oct, Webscale-RL: Automated Data Pipeline for Scaling RL Data to Pretraining Levels, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.06499
6 Oct, Learning on the Job: Test-Time Curricula for Targeted Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.04786
25 Sep, Tree Search for LLM Agent Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.21240
23 Sep, Reinforcement Learning on Pre-Training Data, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.19249
28 Aug, Pref-GRPO: Pairwise Preference Reward-based GRPO for Stable Text-to-Image Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.20751
7 Aug, On the Generalization of SFT: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective with Reward Rectification, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.05629
30 Jul, Efficient Differentially Private Fine-Tuning of LLMs via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.22565
26 Jul, Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.19849
25 Jul, Group Sequence Policy Optimization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.18071
8 Jul, The Delta Learning Hypothesis: Preference Tuning on Weak Data can Yield Strong Gains, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.06187
7 Jul, Pre-Trained Policy Discriminators are General Reward Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.05197
- Other Inference-Time Scaling Methods
Similar to how reinforcement learning is not limited to improving reasoning, inference-time scaling is also not just about improved reasoning. Instead, it is also a general approach for improving LLM efficiency and deployment-time performance.
This section covers more general inference-time techniques (not specific to reasoning), such as adaptive routing and agent orchestration, memory and KV-cache management, and decoding strategies that improve quality or efficiency without additional training.
Figure 5: Annotated figure from XQuant: Breaking the Memory Wall for LLM Inference with KV Cache Rematerialization
30 Oct, Context Engineering 2.0: The Context of Context Engineering, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.26493
2 Oct, The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Scaling Agents for Computer Use, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.02250
30 Aug, Universal Deep Research: Bring Your Own Model and Strategy, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.00244
28 Aug, Adaptive LLM Routing under Budget Constraints, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.21141
14 Aug, XQuant: Breaking the Memory Wall for LLM Inference with KV Cache Rematerialization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10395
18 Aug, Beyond GPT-5: Making LLMs Cheaper and Better via Performance-Efficiency Optimized Routing, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.12631
12 Aug, A Survey on Parallel Text Generation: From Parallel Decoding to Diffusion Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.08712
6 Jul, LayerCake: Token-Aware Contrastive Decoding within Large Language Model Layers, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.04404
- Model Releases / Technical Reports
This section collects papers on new LLM releases and architectural directions.
The included papers span pure transformer models (Olmo 3), and sparse and hybrid architectures (for example, the sparse attention mechanism in DeepSeek V3.2 and Nemotron 3 Nano’s Mamba-Transformer designs).
Figure 6: The NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Nano transformer-mamba hybrid architecture described in Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Model for Agentic Reasoning
23 Dec, Nemotron 3 Nano: Open, Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Model for Agentic Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.20848
15 Dec, Olmo 3, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.13961
2 Dec, DeepSeek-V3.2: Pushing the Frontier of Open Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.02556
30 Oct, Kimi Linear: An Expressive, Efficient Attention Architecture, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.26692
30 Sep, CWM: An Open-Weights LLM for Research on Code Generation with World Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.02387
17 Sep, Apertus: Democratizing Open and Compliant LLMs for Global Language Environments, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.14233
25 Aug, Hermes 4 Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.18255
8 Aug, GLM-4.5: Agentic, Reasoning, and Coding (ARC) Foundation Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.06471
2 Aug, Motif 2.6B Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.09148
28 Jul, Kimi K2: Open Agentic Intelligence, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.20534
17 Jul, Apple Intelligence Foundation Language Models: Tech Report 2025, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.13575
- Architectures
In this section, I collected architectural and training-time papers aimed at improving efficiency and other aspects that are not necessarily tied to a big open-weight model release.
This includes papers that explore alternatives to standard dense attention, including sliding-window and hybrid attention schemes for long contexts, and normalization-free and energy-based training approaches.
Figure 7: Annotated figure from Stronger Normalization-Free Transformers
31 Dec, mHC: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.24880
11 Dec, Sliding Window Attention Adaptation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10411
11 Dec, Stronger Normalization-Free Transformers, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10938
20 Nov, Nemotron Elastic: Towards Efficient Many-in-One Reasoning LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.16664
12 Nov, DoPE: Denoising Rotary Position Embedding, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.09146
22 Oct, Every Attention Matters: An Efficient Hybrid Architecture for Long-Context Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.19338
14 Oct, Dr.LLM: Dynamic Layer Routing in LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.12773
14 Jul, Mixture-of-Recursions: Learning Dynamic Recursive Depths for Adaptive Token-Level Computation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.10524
10 Jul, Dynamic Chunking for End-to-End Hierarchical Sequence Modeling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.07955
2 Jul, Energy-Based Transformers are Scalable Learners and Thinkers, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.02092
- Efficient Training
This section covers (efficient) training techniques that did not fit neatly into the previous categories: low-rank adaptation, quantization, and large-scale training infrastructure.
Figure 8: Annotated figure from Small Batch Size Training for Language Models: When Vanilla SGD Works, and Why Gradient Accumulation Is Wasteful
9 Oct, Optimal Scaling Needs Optimal Norm, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.03871
29 Sep, Pretraining Large Language Models with NVFP4, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.25149
18 Sep, Pre-training under infinite compute, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.14786
5 Sep, Scaling Performance of Large Language Model Pretraining, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.05258
9 Jul, Small Batch Size Training for Language Models: When Vanilla SGD Works, and Why Gradient Accumulation Is Wasteful, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.07101
8 Jul, SingLoRA: Low Rank Adaptation Using a Single Matrix, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.05566
- Diffusion-Based Language Models
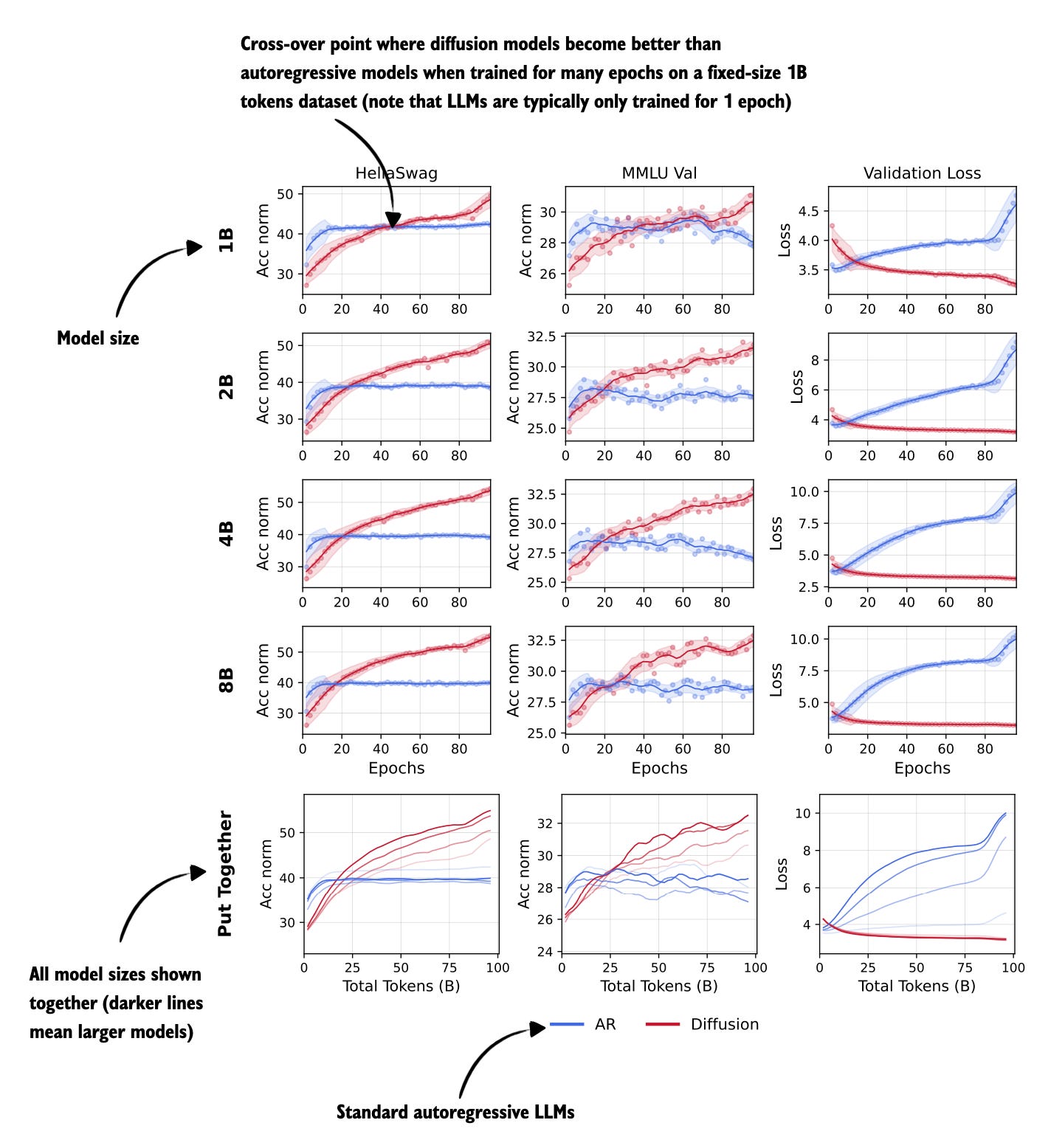
Of course, many researchers are looking for the next thing after transformer-based LLMs. Last year, state space models were considered a hot candidate (which had a comeback in Nemotron 3 Nano’s Mamba-2 layers). This year, the focus was a bit more on language diffusion models. I recently discussed diffusion models for text data in my Beyond Standard LLMs article:
Beyond Standard LLMs SEBASTIAN RASCHKA, PHD · NOVEMBER 4, 2025 Read full story Figure 9: Annotated figure from Diffusion Language Models are Super Data Learners
17 Dec, DEER: Draft with Diffusion, Verify with Autoregressive Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.15176
15 Dec, ReFusion: A Diffusion Large Language Model with Parallel Autoregressive Decoding, https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.13586
12 Nov, TiDAR: Think in Diffusion, Talk in Autoregression, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.08923
5 Nov, Diffusion Language Models are Super Data Learners, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.03276
6 Oct, ParallelBench: Understanding the Trade-offs of Parallel Decoding in Diffusion LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.04767
29 Sep, Learning to Parallel: Accelerating Diffusion Large Language Models via Adaptive Parallel Decoding, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.25188
8 Sep, Revolutionizing Reinforcement Learning Framework for Diffusion Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.06949
27 Aug, Diffusion Language Models Know the Answer Before Decoding, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.19982
4 Aug, Seed Diffusion: A Large-Scale Diffusion Language Model with High-Speed Inference, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.02193
1 Aug, Beyond Fixed: Training-Free Variable-Length Denoising for Diffusion Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.00819
21 Jul, Deep Researcher with Test-Time Diffusion, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.16075
- Multimodal & Vision-Language Models
Multimodal LLMs are a natural extension of text-based LLMs. Besides supporting data formats other than text, one big hope in the research community is that it also unlocks more data that can be used during pre-training to make LLMs “smarter” and more knowledgeable in general. (I think this has not really panned out yet; yes, including images in pre-training is useful if you want your LLM to understand image inputs, but as far as I know, it has not really had a big impact on, say, the text-based problem-solving capabilities of LLMs.)
Anyways, this section brings together research at the intersection of text, image, and video. Also, if you are interested in multimodal LLMs, you may also find my introductory article helpful:
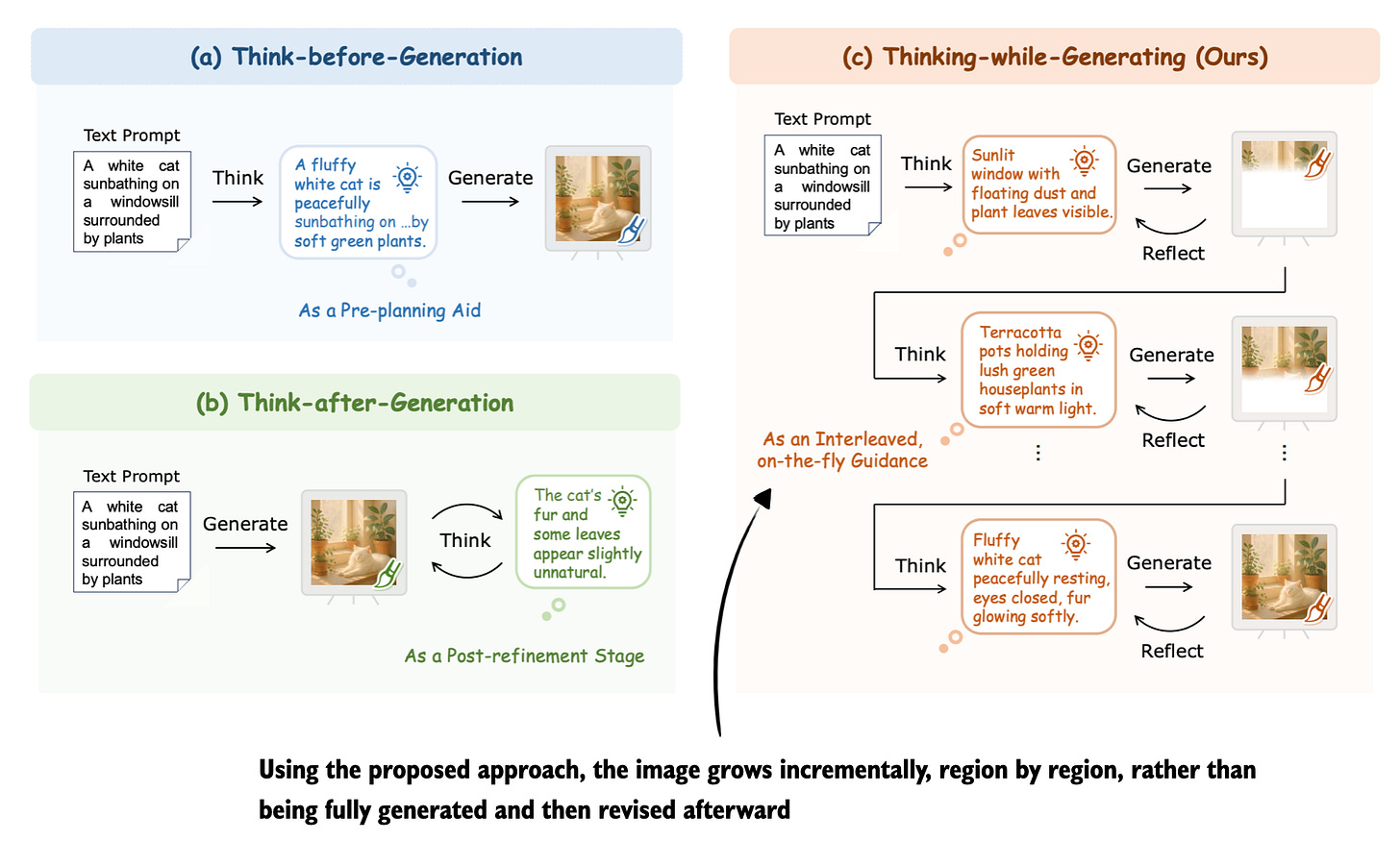
Understanding Multimodal LLMs SEBASTIAN RASCHKA, PHD · NOVEMBER 3, 2024 Read full story Figure 10: Annotated figure from Thinking-while-Generating: Interleaving Textual Reasoning throughout Visual Generation
26 Nov, Qwen3-VL Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.21631
20 Nov, SAM 3: Segment Anything with Concepts, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.16719
20 Nov, Thinking-while-Generating: Interleaving Textual Reasoning throughout Visual Generation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.16671
17 Nov, Large Language Models Meet Extreme Multi-label Classification: Scaling and Multi-modal Framework, https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.13189
14 Aug, We-Math 2.0: A Versatile MathBook System for Incentivizing Visual Mathematical Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10433
14 Aug 2025, NextStep-1: Toward Autoregressive Image Generation with Continuous Tokens at Scale, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10711
11 Aug, Reinforcement Learning in Vision: A Survey, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.08189
4 Aug, Qwen-Image Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.02324
21 Jul, GUI-G2: Gaussian Reward Modeling for GUI Grounding, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.15846
10 Jul, Scaling RL to Long Videos, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.07966
1 Jul, GLM-4.1V-Thinking: Towards Versatile Multimodal Reasoning with Scalable Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.01006
- Data & Pre-training Datasets
Good models need good data. This final section collects papers focused on dataset creation, data quality, pre-training practices, and synthetic data generation.
As the saying goes, data work may not be the flashiest part of AI, but it’s some of the most essential.
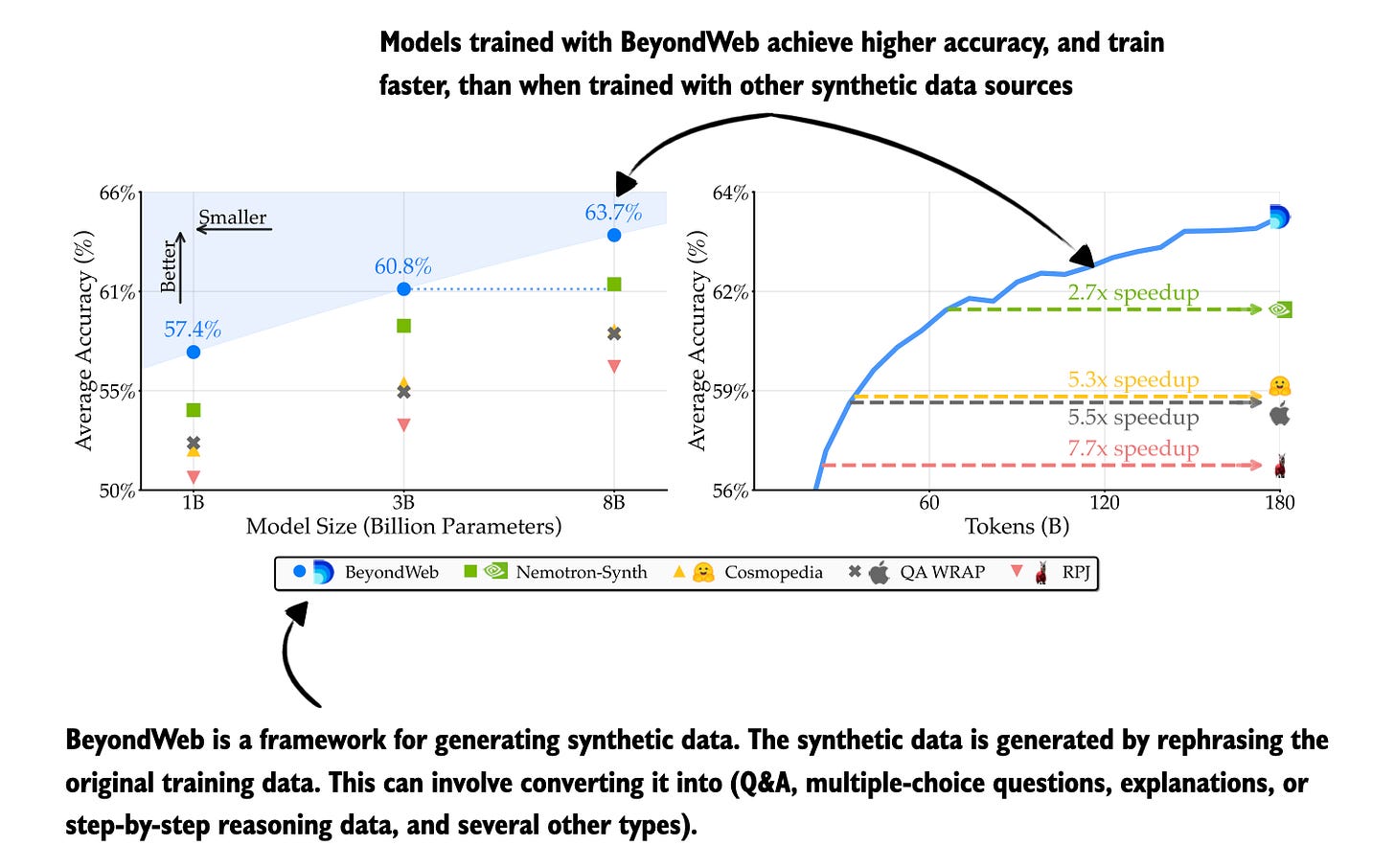
Figure 11: Annotated figure from BeyondWeb: Lessons from Scaling Synthetic Data for Trillion-scale Pretraining
26 Sep, In Their Own Words: Reasoning Traces Tailored for Small Models Make Them Better Reasoners, https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.22230
14 Aug, BeyondWeb: Lessons from Scaling Synthetic Data for Trillion-scale Pretraining, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10975
8 Aug, Deep Ignorance: Filtering Pretraining Data Builds Tamper-Resistant Safeguards into Open-Weight LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.06601
12 Jul, Scaling Laws for Optimal Data Mixtures, https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.09404
I hope you found this list useful for your personal reference. And I hope you perhaps found a handful of interesting reads to check out in more detail.
However, please don’t treat this list as a todo list to work through. It’s more meant as a reference to skim and hopefully helps you find some of the interesting works published this year that may be relevant to projects you are currently working on!
By the way, I was also working on my annual LLM review article, State of LLMs 2025: Progress, Problems, and Predictions, which I published today as well. You can find it here:
The State Of LLMs 2025: Progress, Progress, and Predictions SEBASTIAN RASCHKA, PHD · DECEMBER 30, 2025
As 2025 comes to a close, I want to look back at some of the year’s most important developments in large language models, reflect on the limitations and open problems that remain, and share a few thoughts on what might come next.
Read full story
Thanks so much for subscribing to my Ahead of AI blog and for supporting my work this year. I really appreciate it. Your support makes this work feasible in a very real sense and allows me to keep spending the time needed to write, experiment, and think deeply about these topics!