LLM Research Papers: The 2025 List (January to June)
Subtitle: A topic-organized collection of 200+ LLM research papers from 2025
Date: JUL 19, 2025
URL: https://magazine.sebastianraschka.com/p/llm-research-papers-2025-list-one
Likes: LIKE (1)
Image Count: 11
Images

Figure - Caption: The State of Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
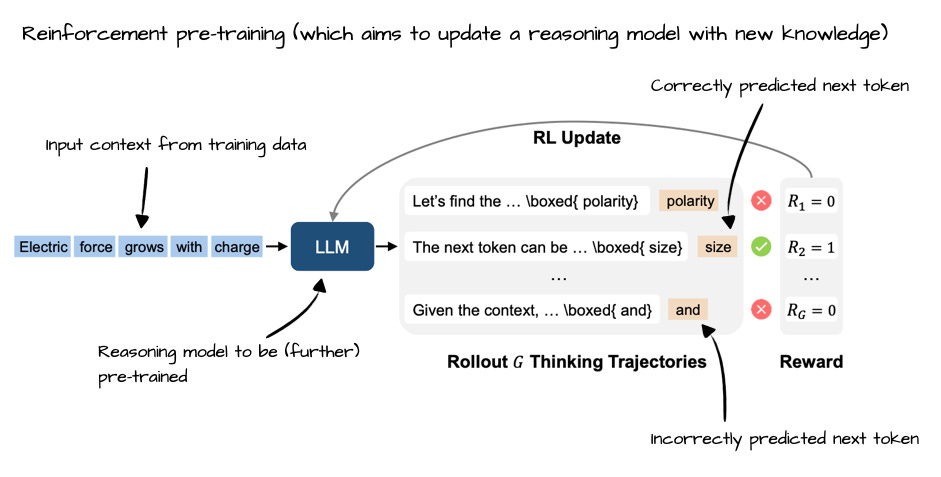
Figure - Caption: Annotated figure from Reinforcement Pre-Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08007
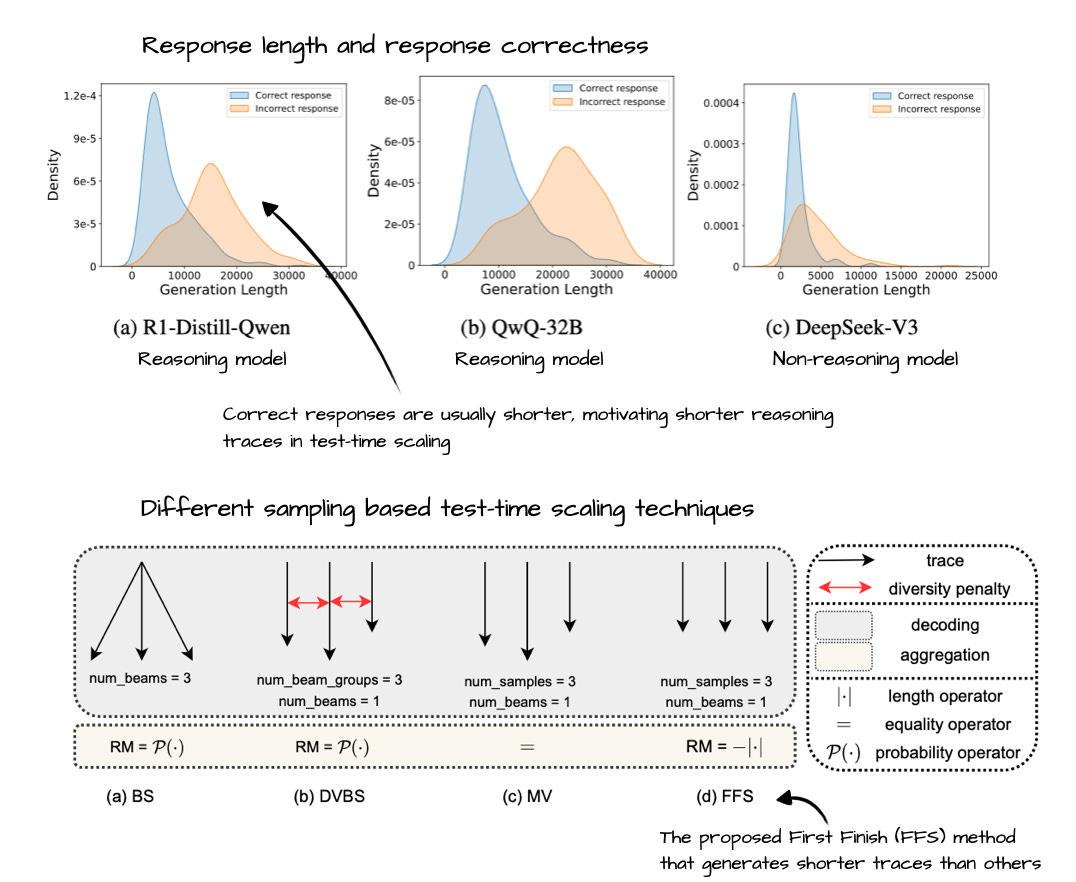
Figure - Caption: Annotated figure from First Finish Search: Efficient Test-Time Scaling in Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.18149
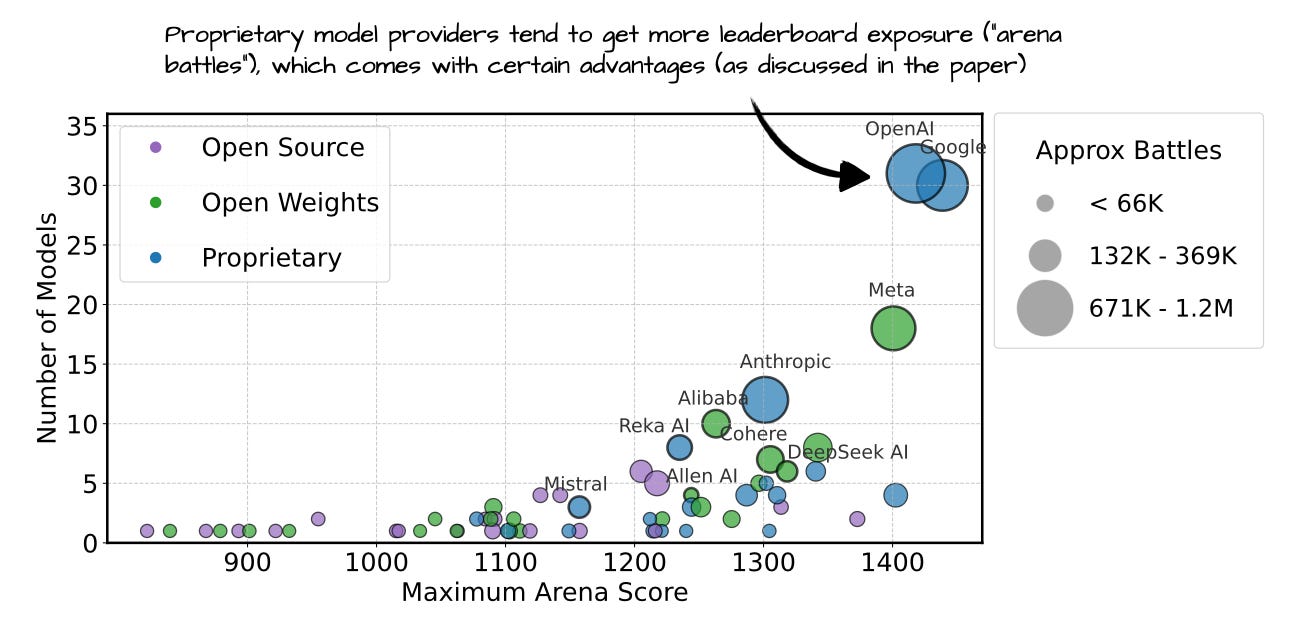
Figure - Caption: Annotated figure from The Leaderboard Illusion, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.20879
Figure 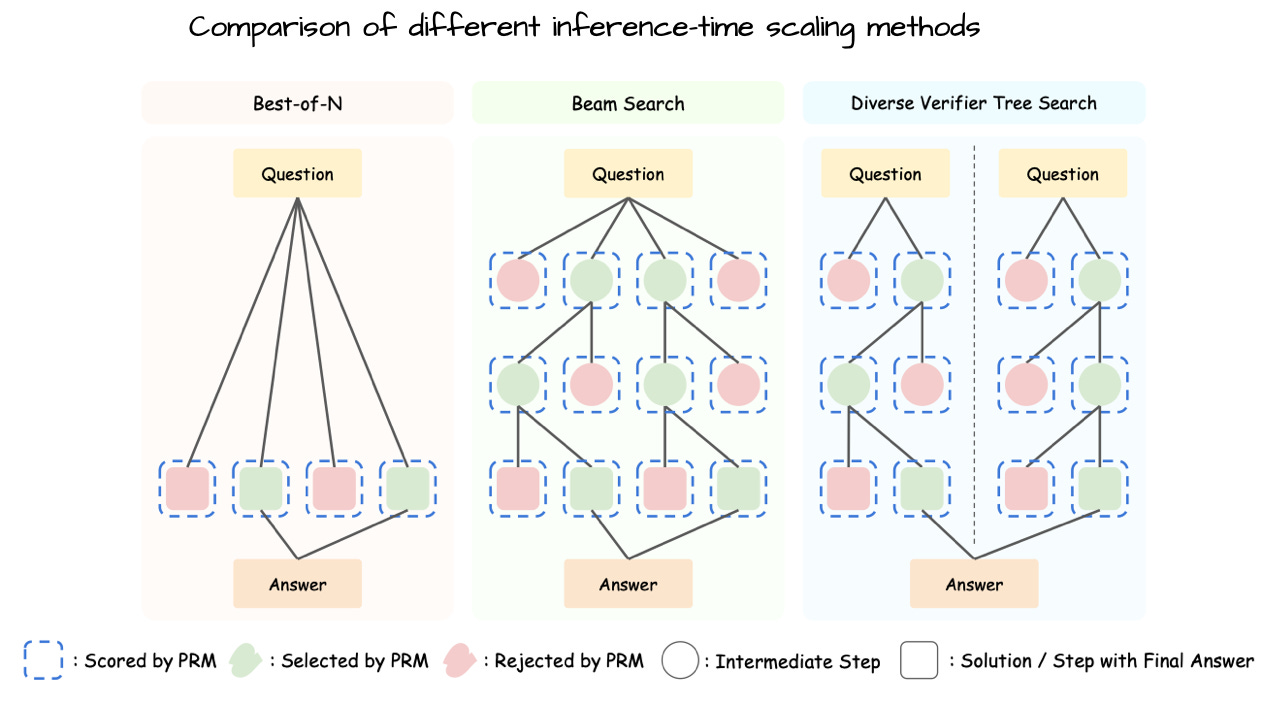
Figure - Caption: Annotated figure from Can 1B LLM Surpass 405B LLM? Rethinking Compute-Optimal Test-Time Scaling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06703
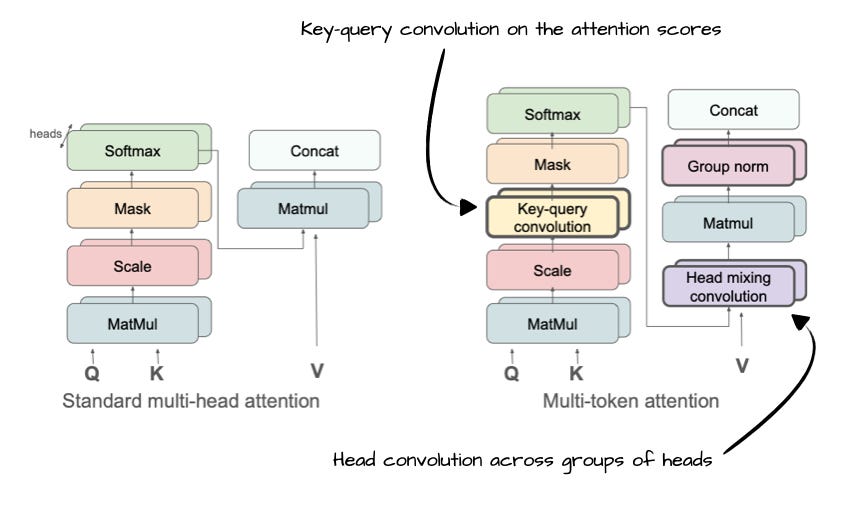
Figure - Caption: Annotated figure from Multi-Token Attention, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.00927
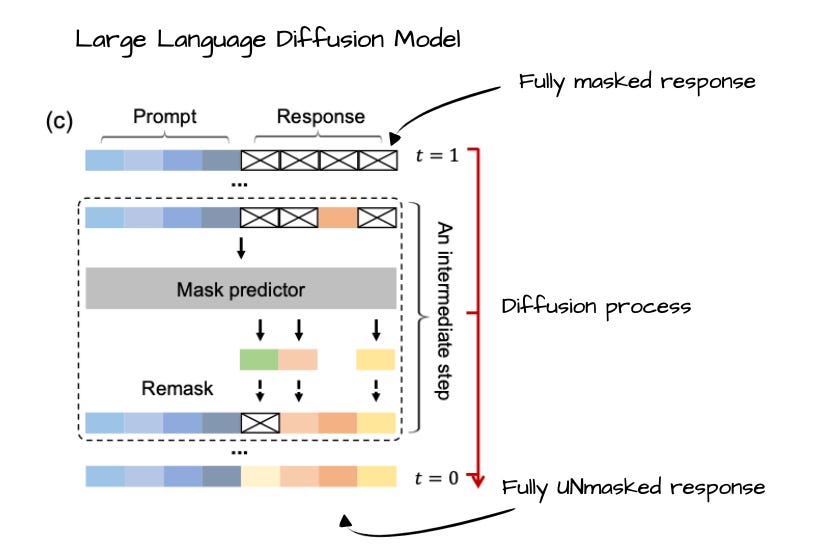
Figure - Caption: Annotated figure from Large Language Diffusion Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.09992

Figure - Caption: Understanding Multimodal LLMs
Figure
- Caption: Annotated figure from SmolVLM: Redefining small and efficient multimodal models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05299
Figure
- Caption: Annotated figure from DeepMath-103K: A Large-Scale, Challenging, Decontaminated, and Verifiable Mathematical Dataset for Advancing Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.11456ion…
Full Text Content
As some of you know, I keep a running list of research papers I (want to) read and reference.
About six months ago, I shared my 2024 list, which many readers found useful. So, I was thinking about doing this again. However, this time, I am incorporating that one piece of feedback kept coming up: “Can you organize the papers by topic instead of date?”
The categories I came up with are:
Reasoning Models
1a. Training Reasoning Models
1b. Inference-Time Reasoning Strategies
1c. Evaluating LLMs and/or Understanding Reasoning
Other Reinforcement Learning Methods for LLMs
Other Inference-Time Scaling Methods
Efficient Training & Architectures
Diffusion-Based Language Models
Multimodal & Vision-Language Models
Data & Pre-training Datasets
Also, as LLM research continues to be shared at a rapid pace, I have decided to break the list into bi-yearly updates. This way, the list stays digestible, timely, and hopefully useful for anyone looking for solid summer reading material.
Please note that this is just a curated list for now. In future articles, I plan to revisit and discuss some of the more interesting or impactful papers in larger topic-specific write-ups. Stay tuned!
Announcement:
It’s summer! And that means internship season, tech interviews, and lots of learning. To support those brushing up on intermediate to advanced machine learning and AI topics, I have made all 30 chapters of my Machine Learning Q and AI book freely available for the summer:
🔗 https://sebastianraschka.com/books/ml-q-and-ai/#table-of-contents
Whether you are just curious and want to learn something new or prepping for interviews, hopefully this comes in handy.
Happy reading, and best of luck if you are interviewing!
- Reasoning Models
This year, my list is very reasoning model-heavy. So, I decided to subdivide it into 3 categories: Training, inference-time scaling, and more general understanding/evaluation.
1a. Training Reasoning Models
This subsection focuses on training strategies specifically designed to improve reasoning abilities in LLMs. As you may see, much of the recent progress has centered around reinforcement learning (with verifiable rewards), which I covered in more detail in a previous article.
The State of Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning SEBASTIAN RASCHKA, PHD · APRIL 19, 2025 Read full story Annotated figure from Reinforcement Pre-Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08007
8 Jan, Towards System 2 Reasoning in LLMs: Learning How to Think With Meta Chain-of-Thought, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.04682
13 Jan, The Lessons of Developing Process Reward Models in Mathematical Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.07301
16 Jan, Towards Large Reasoning Models: A Survey of Reinforced Reasoning with Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.09686
20 Jan, Reasoning Language Models: A Blueprint, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11223
22 Jan, Kimi k1.5: Scaling Reinforcement Learning with LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs//2501.12599
22 Jan, DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.12948
3 Feb, Competitive Programming with Large Reasoning Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06807
5 Feb, Demystifying Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs, Demystifying Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.03373
5 Feb, LIMO: Less is More for Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.03387
5 Feb, Teaching Language Models to Critique via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.03492
6 Feb, Training Language Models to Reason Efficiently, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04463
10 Feb, Exploring the Limit of Outcome Reward for Learning Mathematical Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06781
10 Feb, On the Emergence of Thinking in LLMs I: Searching for the Right Intuition, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06773
11 Feb, LLMs Can Easily Learn to Reason from Demonstrations Structure, not content, is what matters!, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.07374
12 Feb, Fino1: On the Transferability of Reasoning Enhanced LLMs to Finance, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.08127
13 Feb, Adapting Language-Specific LLMs to a Reasoning Model in One Day via Model Merging - An Open Recipe, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.09056
20 Feb, Logic-RL: Unleashing LLM Reasoning with Rule-Based Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.14768
25 Feb, SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.18449
4 Mar, Learning from Failures in Multi-Attempt Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.04808
4 Mar, The First Few Tokens Are All You Need: An Efficient and Effective Unsupervised Prefix Fine-Tuning Method for Reasoning Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.02875
10 Mar, R1-Searcher: Incentivizing the Search Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.05592
10 Mar, LMM-R1: Empowering 3B LMMs with Strong Reasoning Abilities Through Two-Stage Rule-Based RL, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.07536
12 Mar, Search-R1: Training LLMs to Reason and Leverage Search Engines with Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.09516
16 Mar, Towards Hierarchical Multi-Step Reward Models for Enhanced Reasoning in Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.13551
20 Mar, Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning in Small LLMs: What Works and What Doesn’t, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.16219
25 Mar, ReSearch: Learning to Reason with Search for LLMs via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.19470
26 Mar, Understanding R1-Zero-Like Training: A Critical Perspective, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.20783
30 Mar, RARE: Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning Modeling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.23513
31 Mar, Open-Reasoner-Zero: An Open Source Approach to Scaling Up Reinforcement Learning on the Base Model, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.24290
31 Mar, JudgeLRM: Large Reasoning Models as a Judge, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.00050
7 Apr, Concise Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05185
10 Apr, VL-Rethinker: Incentivizing Self-Reflection of Vision-Language Models with Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.08837
11 Apr, Genius: A Generalizable and Purely Unsupervised Self-Training Framework For Advanced Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.08672
13 Apr, Leveraging Reasoning Model Answers to Enhance Non-Reasoning Model Capability, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.09639
21 Apr, Learning to Reason under Off-Policy Guidance, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.14945
22 Apr, Tina: Tiny Reasoning Models via LoRA, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.15777
29 Apr, Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning in Large Language Models with One Training Example, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.20571
30 Apr, Phi-4-Mini-Reasoning: Exploring the Limits of Small Reasoning Language Models in Math, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.21233
2 May, Llama-Nemotron: Efficient Reasoning Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.00949
5 May, RM-R1: Reward Modeling as Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.02387
6 May, Absolute Zero: Reinforced Self-play Reasoning with Zero Data, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.03335
12 May, INTELLECT-2: A Reasoning Model Trained Through Globally Decentralized Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.07291
12 May, MiMo: Unlocking the Reasoning Potential of Language Model – From Pretraining to Posttraining, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.07608
14 May, Qwen3 Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09388
15 May, Beyond ‘Aha!’: Toward Systematic Meta-Abilities Alignment in Large Reasoning Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.10554
19 May, AdaptThink: Reasoning Models Can Learn When to Think, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.13417
19 May, Thinkless: LLM Learns When to Think, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.13379
20 May, General-Reasoner: Advancing LLM Reasoning Across All Domains, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.14652
21 May, Learning to Reason via Mixture-of-Thought for Logical Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.15817
21 May, RL Tango: Reinforcing Generator and Verifier Together for Language Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.15034
23 May, QwenLong-L1: Towards Long-Context Large Reasoning Models with Reinforcement Learning, https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2505.17667
26 May, Enigmata: Scaling Logical Reasoning in Large Language Models with Synthetic Verifiable Puzzles, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.19914
26 May, Learning to Reason without External Rewards, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.19590
29 May, Darwin Godel Machine: Open-Ended Evolution of Self-Improving Agents, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.22954
30 May, Reflect, Retry, Reward: Self-Improving LLMs via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.24726
30 May, ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.24864
2 Jun, Beyond the 80/20 Rule: High-Entropy Minority Tokens Drive Effective Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.01939
3 Jun, Rewarding the Unlikely: Lifting GRPO Beyond Distribution Sharpening, https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2506.02355
9 Jun, Reinforcement Pre-Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08007
10 Jun, RuleReasoner: Reinforced Rule-based Reasoning via Domain-aware Dynamic Sampling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08672
10 Jun, Reinforcement Learning Teachers of Test Time Scaling, https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2506.08388
12 Jun, Magistral, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.10910
12 Jun, Spurious Rewards: Rethinking Training Signals in RLVR, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.10947
16 Jun, AlphaEvolve: A coding agent for scientific and algorithmic discovery, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.13131
17 Jun, Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards Implicitly Incentivizes Correct Reasoning in Base LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.14245
23 Jun, Programming by Backprop: LLMs Acquire Reusable Algorithmic Abstractions During Code Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.18777
26 Jun, Bridging Offline and Online Reinforcement Learning for LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.21495
1b. Inference-Time Reasoning Strategies
This part of the list covers methods that improve reasoning dynamically at test time, without requiring retraining. Often, these papers are focused on trading of computational performance for modeling performance.
Annotated figure from First Finish Search: Efficient Test-Time Scaling in Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.18149
5 Jan, Test-time Computing: from System-1 Thinking to System-2 Thinking, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.02497
8 Jan, rStar-Math: Small LLMs Can Master Math Reasoning with Self-Evolved Deep Thinking, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.04519
9 Jan, Transformer2: Self-adaptive LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.06252
9 Jan, Search-o1: Agentic Search-Enhanced Large Reasoning Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.05366
11 Jan, O1 Replication Journey – Part 3: Inference-time Scaling for Medical Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.06458
16 Jan, OmniThink: Expanding Knowledge Boundaries in Machine Writing through Thinking, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.09751
17 Jan, Evolving Deeper LLM Thinking, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.09891
23 Jan, Can We Generate Images with CoT? Let’s Verify and Reinforce Image Generation Step by Step, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.13926
30 Jan, Thoughts Are All Over the Place: On the Underthinking of o1-Like LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.18585
31 Jan, s1: Simple test-time scaling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.19393
4 Feb, CoAT: Chain-of-Associated-Thoughts Framework for Enhancing Large Language Models Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.02390
5 Feb, Enhancing Reasoning to Adapt Large Language Models for Domain-Specific Applications, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04384
6 Feb, Step Back to Leap Forward: Self-Backtracking for Boosting Reasoning of Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04404
7 Feb, Scaling up Test-Time Compute with Latent Reasoning: A Recurrent Depth Approach, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.05171
9 Feb, LM2: Large Memory Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06049
10 Feb, ReasonFlux: Hierarchical LLM Reasoning via Scaling Thought Templates, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06772
16 Feb, Learning to Reason from Feedback at Test-Time, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.15771
19 Feb, Inner Thinking Transformer: Leveraging Dynamic Depth Scaling to Foster Adaptive Internal Thinking, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.13842
20 Feb, Optimizing Model Selection for Compound AI Systems, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.14815
21 Feb, Minions: Cost-efficient Collaboration Between On-device and Cloud Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.15964
25 Feb, Chain of Draft: Thinking Faster by Writing Less, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.18600
26 Feb, Self-rewarding correction for mathematical reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.19613
6 Mar, START: Self-taught Reasoner with Tools, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.04625
10 Mar, Sketch-of-Thought: Efficient LLM Reasoning with Adaptive Cognitive-Inspired Sketching, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.05179
10 Mar, Optimizing Test-Time Compute via Meta Reinforcement Fine-Tuning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.07572
11 Mar, Self-Taught Self-Correction for Small Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.08681
13 Mar, Thinking Machines: A Survey of LLM based Reasoning Strategies, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.10814
17 Mar, ϕ-Decoding: Adaptive Foresight Sampling for Balanced Inference-Time Exploration and Exploitation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.13288
14 Apr, Reasoning Models Can Be Effective Without Thinking, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.09858
18 Apr, Think Deep, Think Fast: Investigating Efficiency of Verifier-free Inference-time-scaling Methods, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.14047
20 Mar, Stop Overthinking: A Survey on Efficient Reasoning for Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.16419
21 Mar, Chain-of-Tools: Utilizing Massive Unseen Tools in the CoT Reasoning of Frozen Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.16779
23 Mar, AgentRxiv: Towards Collaborative Autonomous Research, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.18102
25 Mar, Think Twice: Enhancing LLM Reasoning by Scaling Multi-round Test-time Thinking, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.19855
26 Mar, Open Deep Search: Democratizing Search with Open-source Reasoning Agents, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.20201
27 Mar, MemInsight: Autonomous Memory Augmentation for LLM Agents, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.21760
28 Mar, Think Before Recommend: Unleashing the Latent Reasoning Power for Sequential Recommendation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.22675
29 Mar, Efficient Inference for Large Reasoning Models: A Survey, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.23077
1 Apr, Z1: Efficient Test-time Scaling with Code, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.00810
2 Apr, DeepSeek-R1 Thoughtology: Let’s
4 Apr, LightPROF: A Lightweight Reasoning Framework for Large Language Model on Knowledge Graph, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.03137
7 Apr, T1: Tool-integrated Self-verification for Test-time Compute Scaling in Small Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.04718
8 Apr, Hogwild! Inference: Parallel LLM Generation via Concurrent Attention, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.06261
14 Apr, Heimdall: test-time scaling on the generative verification, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.10337
14 Apr, Reasoning Models Can Be Effective Without Thinking, https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2504.09858
17 Apr, Antidistillation Sampling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.13146
23 May, First Finish Search: Efficient Test-Time Scaling in Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.18149
30 May, HardTests: Synthesizing High-Quality Test Cases for LLM Coding, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.24098
30 May, AlphaOne: Reasoning Models Thinking Slow and Fast at Test Time, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.24863
3 Jun, OThink-R1: Intrinsic Fast/Slow Thinking Mode Switching for Over-Reasoning Mitigation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.02397
10 Jun, Wait, We Don’t Need to “Wait”! Removing Thinking Tokens Improves Reasoning Efficiency, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08343
1c. Evaluating LLMs and/or Understanding Reasoning
In chapter one of my “Reasoning from Scratch” book, I discussed that reasoning in LLMs is a form of simulating reasoning without explicit rules. And, at first glance, those “reasoning processes in LLMs may closely resemble human thought, particularly in how intermediate steps are articulated.”
However, as I wrote back then in March, I believe “that current LLM reasoning is primarily based on patterns learned from extensive statistical associations present in training data, rather than explicit internal cognitive structures or conscious reflection.” And honestly, there is nothing wrong with that, as it clearly works well in practice and provides value.
Now, a few weeks ago, a research team at Apple published a new paper that provides some evidence for such a claim: The Illusion of Thinking: Understanding the Strengths and Limitations of Reasoning Models via the Lens of Problem Complexity. This paper jumpstarted a big discussion about whether LLMs are “just” statistical pattern matchers etc.
Note that this is an interesting study, but it is just one (more or less limited) study. We may need more papers and more studies to say anything with certainty. Also, as I mentioned earlier, the fact that LLMs provide so much value is an already big win (and whether LLMs reason similar to humans is only a secondary concern).
That being said, in this section, I collected papers that try to analyze (or evaluate) reasoning models in various ways, which is useful to refine and improve the current generation of LLM-based reasoning models.
Annotated figure from The Leaderboard Illusion, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.20879
24 Jan, Humanity’s Last Exam, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14249
12 Feb, The Danger of Overthinking: Examining the Reasoning-Action Dilemma in Agentic Tasks, https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2502.08235
17 Feb, SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.12115
18 Feb, How Do LLMs Acquire New Knowledge? A Knowledge Circuits Perspective on Continual Pre-Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.11196
26 Feb, BIG-Bench Extra Hard, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.19187
26 Feb, Can Large Language Models Detect Errors in Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.19361
24 Mar, I Have Covered All the Bases Here: Interpreting Reasoning Features in Large Language Models via Sparse Autoencoders, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.18878
27 Mar, Challenging the Boundaries of Reasoning: An Olympiad-Level Math Benchmark for Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.21380
2 Apr, PaperBench: Evaluating AI’s Ability to Replicate AI Research, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.01848
3 Apr, Why do LLMs attend to the first token?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.02732
3 Apr, Generative Evaluation of Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.02810
5 Apr, Rethinking Reflection in Pre-Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.04022
7 Apr, Quantization Hurts Reasoning? An Empirical Study on Quantized Reasoning Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.04823
9 Apr, Missing Premise exacerbates Overthinking: Are Reasoning Models losing Critical Thinking Skill?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.06514
14 Apr, xVerify: Efficient Answer Verifier for Reasoning Model Evaluations, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.10481
14 Apr, How Instruction and Reasoning Data shape Post-Training: Data Quality through the Lens of Layer-wise Gradients, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.10766
18 Apr, Does Reinforcement Learning Really Incentivize Reasoning Capacity in LLMs Beyond the Base Model?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.13837
18 Apr, Does Reinforcement Learning Really Incentivize Reasoning Capacity in LLMs Beyond the Base Model?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.13837
29 Apr, The Leaderboard Illusion, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.20879
29 May, Are Reasoning Models More Prone to Hallucination?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.23646
2 Jun, Knowledge or Reasoning? A Close Look at How LLMs Think Across Domains, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.02126
10 Jun, Your Brain on ChatGPT: Accumulation of Cognitive Debt when Using an AI Assistant for Essay Writing Task, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08872
18 Jun, Leaky Thoughts: Large Reasoning Models Are Not Private Thinkers, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.15674
- Other Reinforcement Learning Methods for LLMs
Beyond reasoning-focused reinforcement learning, there is of course still the broader topic of aligning LLMs with human preferences using reinforcement learning.
This section captures papers that explore alternative alignment techniques, preference modeling, test-time optimization, and large-scale infrastructure for reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF).
These efforts provide context for where reinforcement learning is going in the LLM landscape (beyond just making models reason better).
3 Jan, SDPO: Segment-Level Direct Preference Optimization for Social Agents, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.01821
4 Jan, REINFORCE++: A Simple and Efficient Approach for Aligning Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.03262
22 Jan, Test-Time Preference Optimization: On-the-Fly Alignment via Iterative Textual Feedback, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.12895
28 Jan, SFT Memorizes, RL Generalizes: A Comparative Study of Foundation Model Post-training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.17161
30 Jan, Diverse Preference Optimization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.18101
3 Feb, The Differences Between Direct Alignment Algorithms are a Blur, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.01237
7 Feb, Probabilistic Artificial Intelligence, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.05244
20 Feb, MLGym: A New Framework and Benchmark for Advancing AI Research Agents, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.14499
18 Mar, DAPO: An Open-Source LLM Reinforcement Learning System at Scale, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.14476
28 Mar, Exploring Data Scaling Trends and Effects in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.22230
31 Mar, Crossing the Reward Bridge: Expanding RL with Verifiable Rewards Across Diverse Domains, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.23829
22 Apr, TTRL: Test-Time Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.16084
15 May, WorldPM: Scaling Human Preference Modeling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.10527
28 May, The Entropy Mechanism of Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.22617
29 May, LlamaRL: A Distributed Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning Framework for Efficient Large-scale LLM Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.24034
12 Jun, Self-Adapting Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.10943
- Other Inference-Time Scaling Methods
Similar to how reinforcement learning is not just for reasoning, inference-time scaling is also not just for reasoning. Inference-time scaling is a general approach for improving LLM efficiency and performance.
This section includes work on token-efficient methods, memory management, and so forth that help models perform better with smarter resource use.
Annotated figure from Can 1B LLM Surpass 405B LLM? Rethinking Compute-Optimal Test-Time Scaling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06703
16 Jun, MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.13585
3 Apr, Inference-Time Scaling for Generalist Reward Modeling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.02495
31 Mar, What, How, Where, and How Well? A Survey on Test-Time Scaling in Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.24235
24 Mar, Video-T1: Test-Time Scaling for Video Generation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.18942
6 Mar, Dedicated Feedback and Edit Models Empower Inference-Time Scaling for Open-Ended General-Domain Tasks, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.04378
27 Feb, LongRoPE2: Near-Lossless LLM Context Window Scaling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.20082
20 Feb, S*: Test Time Scaling for Code Generation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.14382
12 Feb, InfiniteHiP: Extending Language Model Context Up to 3 Million Tokens on a Single GPU, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.08910
11 Feb, Auditing Prompt Caching in Language Model APIs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.07776
10 Feb, Can 1B LLM Surpass 405B LLM? Rethinking Compute-Optimal Test-Time Scaling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06703
- Efficient Training & Architectures
This section covers a mix between LLM architectures announcements and small architecture innovations. But it also covers (efficient) training techniques that did not fit neatly into the previous categories: low-rank adaptation, quantization, and large-scale training infrastructure.
Annotated figure from Multi-Token Attention, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.00927
26 Jan, Qwen2.5-1M Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.15383
24 Feb, Make LoRA Great Again: Boosting LoRA with Adaptive Singular Values and Mixture-of-Experts Optimization Alignment, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.16894
25 Feb, The FFT Strikes Back: An Efficient Alternative to Self-Attention, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.18394
26 Feb, NeoBERT: A Next-Generation BERT, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.19587
2 Mar, Babel: Open Multilingual Large Language Models Serving Over 90% of Global Speakers, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.00865
3 Mar, Forgetting Transformer: Softmax Attention with a Forget Gate, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.02130
7 Mar, EuroBERT: Scaling Multilingual Encoders for European Languages, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.05500
10 Mar, DistiLLM-2: A Contrastive Approach Boosts the Distillation of LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.07067
12 Mar, Communication-Efficient Language Model Training Scales Reliably and Robustly: Scaling Laws for DiLoCo, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.09799
13 Mar, Transformers without Normalization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.10622
14 Mar, A Review of DeepSeek Models’ Key Innovative Techniques, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.11486
18 Mar, RWKV-7 “Goose” with Expressive Dynamic State Evolution, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.14456
25 Mar, Gemma 3 Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.19786
31 Mar, NoProp: Training Neural Networks without Back-propagation or Forward-propagation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.24322
31 Mar, TransMamba: Flexibly Switching between Transformer and Mamba, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.24067
1 Apr, Multi-Token Attention, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.00927
1 Apr, Command A: An Enterprise-Ready Large Language Model, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.00698
3 Apr, ZClip: Adaptive Spike Mitigation for LLM Pre-Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.02507
11 Apr, ModernBERT or DeBERTaV3? Examining Architecture and Data Influence on Transformer Encoder Models Performance, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.08716
16 Apr, BitNet b1.58 2B4T Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.12285
25 Apr, BitNet v2: Native 4-bit Activations with Hadamard Transformation for 1-bit LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.18415
4 May, Practical Efficiency of Muon for Pretraining, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.02222
4 May, An Empirical Study of Qwen3 Quantization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.02214
17 May, Model Merging in Pre-training of Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.12082
17 May, Chain-of-Model Learning for Language Model, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.11820
20 May, Scaling Law for Quantization-Aware Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.14302
23 May, H2: Towards Efficient Large-Scale LLM Training on Hyper-Heterogeneous Cluster over 1,000 Chips, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.17548
2 Jun, Why Gradients Rapidly Increase Near the End of Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.02285
6 Jun, Text-to-LoRA: Instant Transformer Adaption, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.06105
16 Jun, Arctic Long Sequence Training: Scalable And Efficient Training For Multi-Million Token Sequences, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.13996
23 Jun, Is There a Case for Conversation Optimized Tokenizers in Large Language Models?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.18674
24 Jun, Outlier-Safe Pre-Training for Robust 4-Bit Quantization of Large Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.19697
- Diffusion-Based Language Models
Of course, many researchers are looking for the next thing after transformer-based LLMs. Last year, state space models were considered a hot candidate. This year, it’s language diffusion models. (I will likely cover them in more detail in a future article.)
Annotated figure from Large Language Diffusion Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.09992
14 Feb, Large Language Diffusion Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.09992
12 Mar, Block Diffusion: Interpolating Between Autoregressive and Diffusion Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.09573
8 Apr, DDT: Decoupled Diffusion Transformer, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05741
16 Apr, d1: Scaling Reasoning in Diffusion Large Language Models via Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.12216
20 May, Diffusion vs. Autoregressive Language Models: A Text Embedding Perspective, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.15045
22 May, LaViDa: A Large Diffusion Language Model for Multimodal Understanding, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.16839
12 Jun, The Diffusion Duality, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.10892
17 Jun, Mercury: Ultra-Fast Language Models Based on Diffusion, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.17298
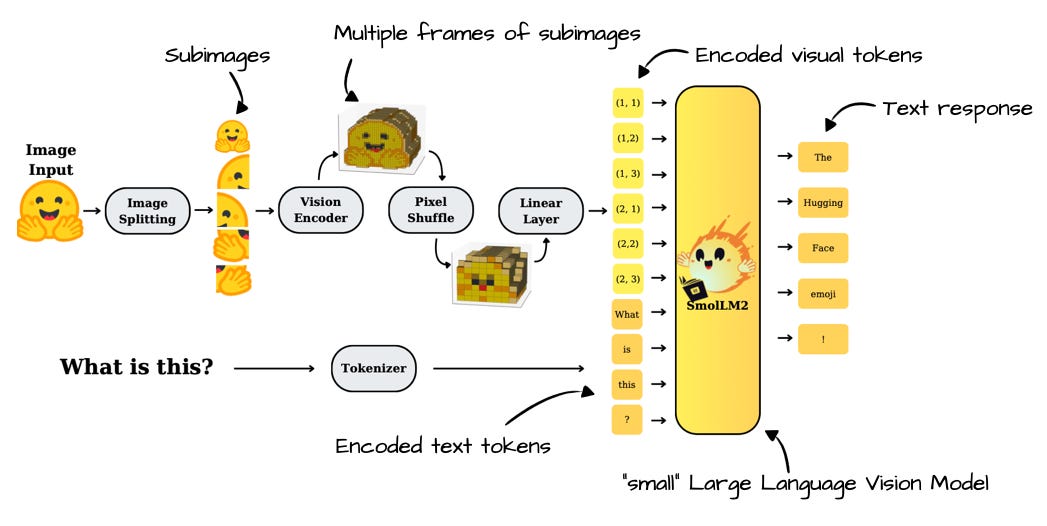
- Multimodal & Vision-Language Models
Multimodal LLMs are a natural extension of text-based LLMs. Besides supporting data formats other than text, one big hope in the research community is that it also unlocks more data that can be used during pre-training to make LLMs “smarter” and more knowledgeable in general. (I think this has not really panned out yet; yes, including images in pre-training is useful if you want your LLM to understand image inputs, but as far as I know, it has not really had a big impact on, say, the text-based problem-solving capabilities of LLMs.)
Anyways, This section brings together research at the intersection of text, image, and video. Also, if you are interested in multimodal LLMs, you may also find my introductory article helpful:
Understanding Multimodal LLMs SEBASTIAN RASCHKA, PHD · NOVEMBER 3, 2024
It was a wild two months. There have once again been many developments in AI research, with two Nobel Prizes awarded to AI and several interesting research papers published.
Read full story Annotated figure from SmolVLM: Redefining small and efficient multimodal models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05299
9 Jan, The GAN is dead; long live the GAN! A Modern GAN Baseline, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.05441
29 Jan, Janus-Pro: Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation with Data and Model Scaling, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.17811
7 Feb, VideoRoPE: What Makes for Good Video Rotary Position Embedding?, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.05173
3 Mar, Phi-4-Mini Technical Report: Compact yet Powerful Multimodal Language Models via Mixture-of-LoRAs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.01743
3 Mar, Visual-RFT: Visual Reinforcement Fine-Tuning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.01785
7 Mar, R1-Zero’s “Aha Moment” in Visual Reasoning on a 2B Non-SFT Model, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.05132
7 Mar, Token-Efficient Long Video Understanding for Multimodal LLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.04130
10 Mar, MM-Eureka: Exploring Visual Aha Moment with Rule-based Large-scale Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.07365
19 Mar, TULIP: Towards Unified Language-Image Pretraining, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.15485
20 Mar, OThink-MR1: Stimulating multimodal generalized reasoning capabilities via dynamic reinforcement learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.16081
25 Mar, Scaling Vision Pre-Training to 4K Resolution, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.19903
26 Mar, Qwen2.5-Omni Technical Report, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.20215
27 Mar, Video-R1: Reinforcing Video Reasoning in MLLMs, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.21776
31 Mar, Advances and Challenges in Foundation Agents: From Brain-Inspired Intelligence to Evolutionary, Collaborative, and Safe Systems, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.01990
1 Apr, MergeVQ: A Unified Framework for Visual Generation and Representation with Disentangled Token Merging and Quantization, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.00999
3 Apr, GPT-ImgEval: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Diagnosing GPT4o in Image Generation, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.02782
7 Apr, SmolVLM: Redefining small and efficient multimodal models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05299
7 Apr, One-Minute Video Generation with Test-Time Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05298
14 Apr, InternVL3: Exploring Advanced Training and Test-Time Recipes for Open-Source Multimodal Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.10479
4 Jun, Advancing Multimodal Reasoning: From Optimized Cold Start to Staged Reinforcement Learning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.04207
11 Jun, V-JEPA 2: Self-Supervised Video Models Enable Understanding, Prediction and Planning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.09985
19 Jun, GenRecal: Generation after Recalibration from Large to Small Vision-Language Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.15681
- Data & Pre-training Datasets
Good models need good data. This final section collects papers focused on dataset creation, data quality, pre-training practices, and synthetic data generation.
As the saying goes, data work may not be the flashiest part of AI, but it’s some of the most essential.
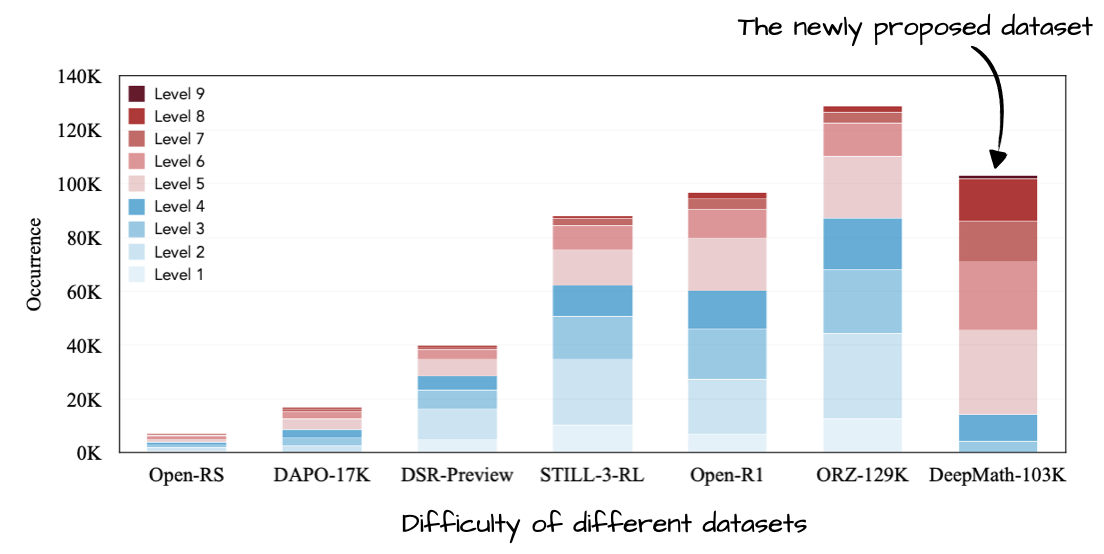
Annotated figure from DeepMath-103K: A Large-Scale, Challenging, Decontaminated, and Verifiable Mathematical Dataset for Advancing Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.11456ion…
14 Jan, Towards Best Practices for Open Datasets for LLM Training, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.08365
31 Jan, Text Data Augmentation for Large Language Models: A Comprehensive Survey of Methods, Challenges, and Opportunities, https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.18845
18 Feb, NaturalReasoning: Reasoning in the Wild with 2.8M Challenging Questions, https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.13124
11 Mar, Feature-Level Insights into Artificial Text Detection with Sparse Autoencoders, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.03601
18 Mar, Synthetic Data Generation Using Large Language Models: Advances in Text and Code, https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.14023
3 Apr, MegaMath: Pushing the Limits of Open Math Corpora, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.02807
9 Apr, OLMoTrace: Tracing Language Model Outputs Back to Trillions of Training Tokens, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.07096
15 Apr, DeepMath-103K: A Large-Scale, Challenging, Decontaminated, and Verifiable Mathematical Dataset for Advancing Reasoning, https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.11456
20 May, Large Language Models for Data Synthesis, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.14752
30 May, How much do language models memorize?, https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2505.24832
4 Jun, OpenThoughts: Data Recipes for Reasoning Models, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.04178
5 Jun, The Common Pile v0.1: An 8TB Dataset of Public Domain and Openly Licensed Text, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.05209
17 Jun, Essential-Web v1.0: 24T tokens of organized web data, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.14111
26 Jun, Where to find Grokking in LLM Pretraining? Monitor Memorization-to-Generalization without Test, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.21551
26 Jun, FineWeb2: One Pipeline to Scale Them All – Adapting Pre-Training Data Processing to Every Language, https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.20920
I hope you found this list useful for your personal reference. And I hope you perhaps found a handful of interesting reads to check out in more detail. As mentioned earlier, I will share some more detailed discussions involving some of these papers in future articles.
Ahead of AI is a reader-supported, independent project dedicated to providing educational insights and updates on AI and machine learning. By subscribing, you directly support this independent research and help me continue delivering high-quality, unbiased content.
Subscribed